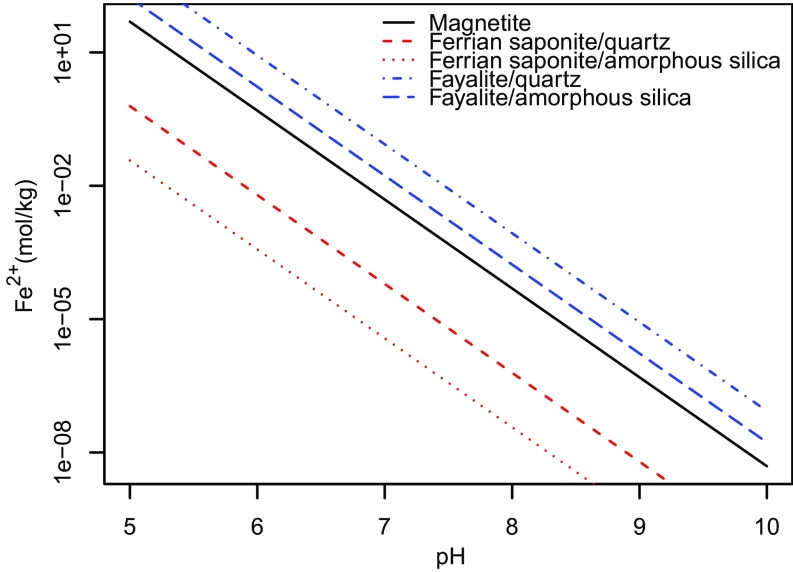
Fig. S1.
Thermodynamic stability diagram showing the Fe2+ concentration required to be in equilibrium with various minerals and silica activities ranging from quartz to amorphous silica, as a function of pH. Lines show saturation values at 10 °C and a salinity of 10 g/kg. Minerals are supersaturated above their respective equilibrium lines. All thermodynamic data come from ref. 53 with the exception of Fe saponite (Na0.35Fe3Al0.35Si3.65O10OH2) determined in ref. 16. In drawing the stability boundaries for magnetite, redox state is set at the magnetite/hematite boundary, as detailed in the main text. In defining equilibrium lines for ferrian saponite, Al3+ is set to saturation with respect to albite, which is reasonable given that the Sheepbed contains ∼20 wt % plagioclase feldspar (9).