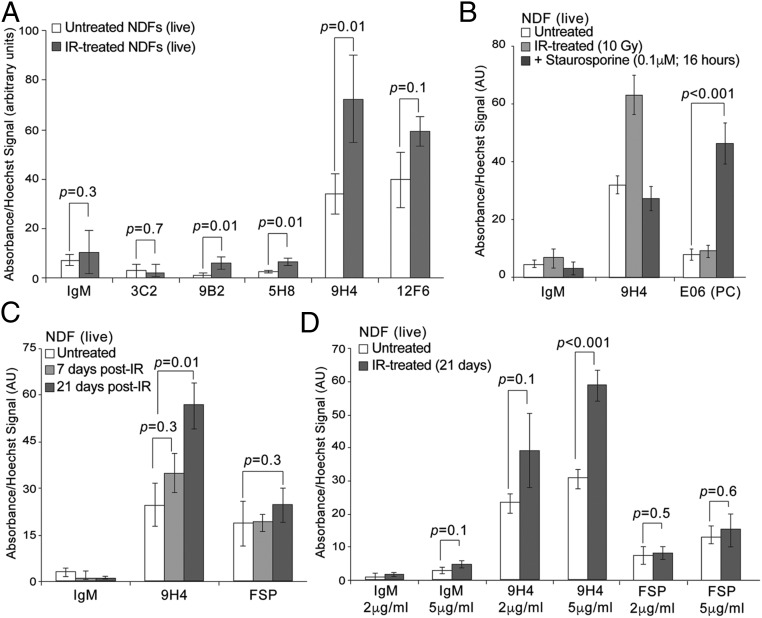
Fig. 1.
Generation and isolation of antibodies against senescent cells. (A) SACE analysis using IgM clones to detect immunoreactivity toward live senescent NDF cells. An HRP-conjugated IgM-specific secondary antibody was used in conjunction with TMB substrate for colorimetric ELISA reading at an absorbance of 450 nm to detect binding of IgMs to the surface of cells. DNA was stained with cell permeable Hoechst to normalize TMB absorbance values. Values (arbitrary units) and SDs were calculated from triplicates. An unpaired Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. (B) SACE analysis (as in A) using whole-molecule mouse IgM (negative control) or the IgM antibodies 9H4 and E06 to detect immunoreactivity toward live untreated, senescent, or staurosporine-treated (0.1 μM for 16 h) NDF cells. Values (arbitrary units) and SDs were calculated from triplicates. An unpaired Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. (C) SACE analysis (as in A) using whole-molecule mouse IgM (negative control) or the IgM antibodies 9H4 and anti-FSP to detect immunoreactivity toward live senescent NDF cells. Values (arbitrary units) and SDs were calculated from triplicates. An unpaired Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. (D) SACE analysis (as in A) using whole-molecule mouse IgM (negative control) or the IgM antibodies 9H4 and anti-FSP to detect antibody dose-dependency and immunoreactivity toward live senescent NDF cells. Values (arbitrary units) and SDs were calculated from triplicates. An unpaired Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis.