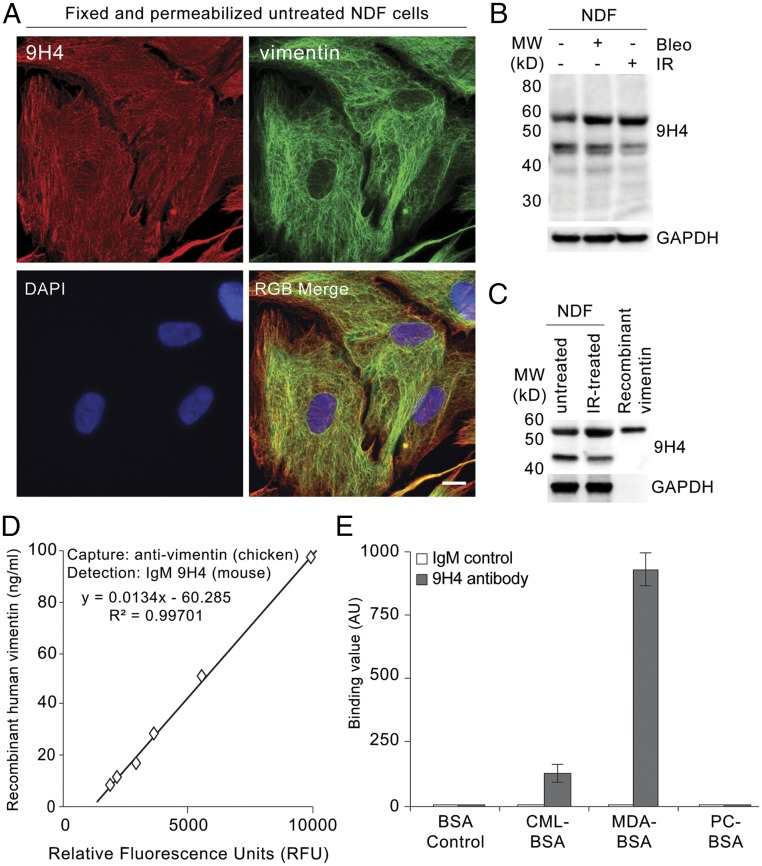
Fig. 2.
IgM 9H4 clone recognizes the intermediate filament vimentin. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of 2% PFA fixed and Triton X-100 permeabilized untreated NDF cells stained with IgM 9H4 clone (red) and an antivimentin antibody (green). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (B) Immunoblot of WCE from untreated, IR-treated, or bleomycin-treated NDFs using IgM 9H4, as indicated. GAPDH is used as loading control. (C) Immunoblot of WCE from untreated or IR-treated NDFs and recombinant human vimentin using IgM 9H4, as indicated. GAPDH is used as loading control. (D) Sandwich ELISA measuring increasing levels of recombinant human vimentin. A polyclonal antivimentin (chicken) antibody was used as a capture antibody and IgM 9H4 was used to detect vimentin. (E) Polyreactivity of IgM 9H4 or whole-molecule IgM was measured by direct ELISA. Binding value was assessed for each antibody by testing their binding to BSA or the indicated BSA-conjugated haptens. Values (arbitrary units) and SDs were calculated from triplicates. An unpaired Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis.