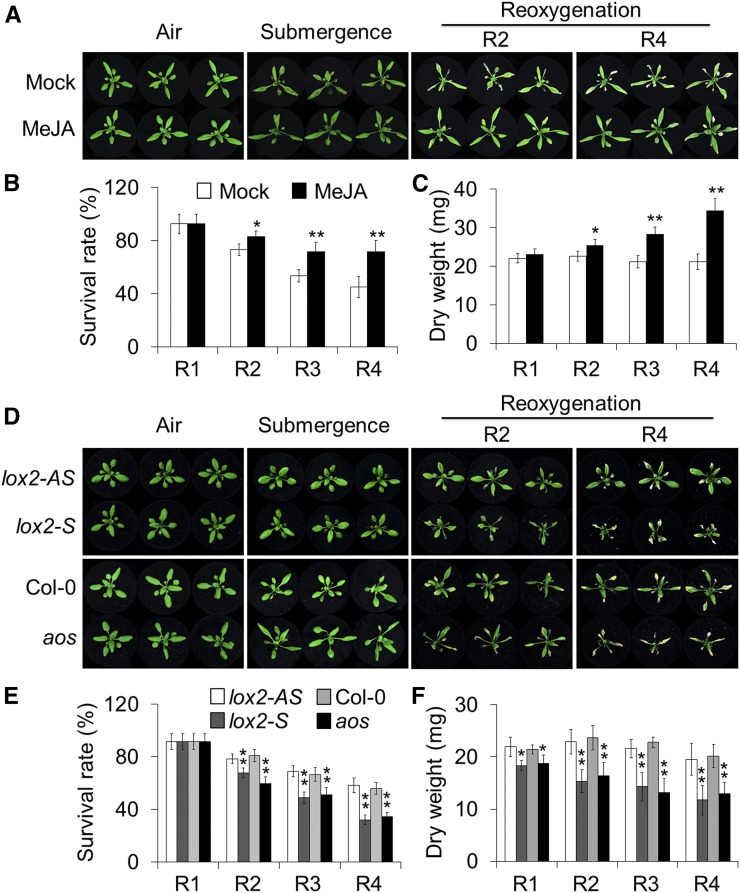
Figure 2.
Involvement of JA biosynthesis in the plant response to reoxygenation. A to C, phenotypes (A), survival rates (B), and dry weights (C) of wild-type plants treated with exogenous MeJA and then subjected to submergence and reoxygenation. Four-week-old wild-type plants were pretreated with 100 μm MeJA or mock solution (0.1% ethanol in water) for 24 h. Images were photographed before submergence (Air) and after 48 h dark submergence (Submergence) followed by reoxygenation for 1, 2, 3, and 4 d (R1, R2, R3, and R4). D to F, phenotypes (D), survival rates (E), and dry weights (F) of lox-S and aos mutants and their corresponding controls (lox2-AS and Col-0; 4-week-old) before submergence (Air) and after 48 h dark submergence (Submergence) followed by reoxygenation for 1, 2, 3, and 4 d (R1, R2, R3, and R4). The data in B, C, E, and F are means ± sd (n = 3 independent experiments). For each experiment, at least 15 plants were used for each genotype. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the mock treatment or wild-type control (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test).