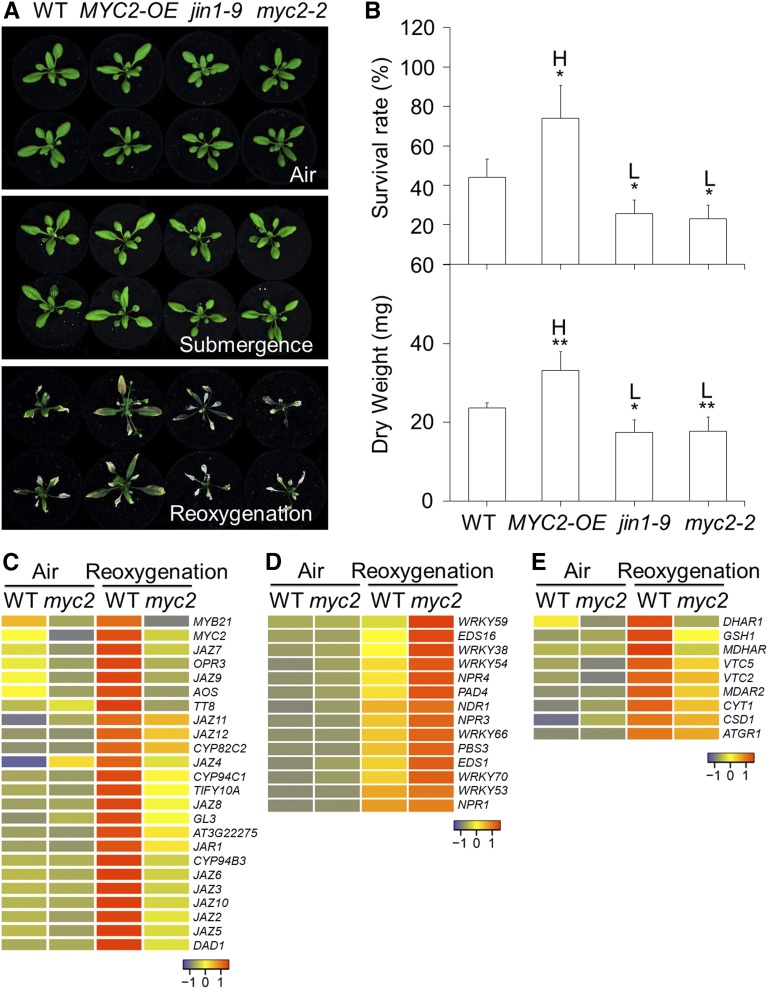
Figure 4.
MYC2 is a key transcription factor in the regulation of plant tolerance to reoxygenation and antioxidant synthesis gene expression. A, Phenotypes of wild type (WT), MYC2-OE, jin1-9, and myc2-2 before submergence (Air) and after 2 d dark submergence (Submergence) followed by 4 d of reoxygenation (Reoxygenation). B, Survival rates (top) and dry weights (bottom) of WT, MYC2-OE, jin1-9, and myc2-2 after 2 d dark submergence followed by a 4 d reoxygenation period. The data are means ± sd (n = 3 independent experiments). For each experiment, 15 plants were used for each genotype. Asterisks indicate significant differences from WT (*P < 0.05 by Student’s t test). “H” and “L” indicate significantly higher or lower values, respectively, than in the WT. C to E, Hierarchical cluster analyses applied to the 24 DEGs (more than 2-fold and FDR < 0.01) in the JA pathway (C), 14 DEGs in the SA pathway (D), and nine DEGs of the antioxidant syntheses (E) in myc2-2 mutant in comparison with WT before treatment (Air) and upon 3 h of reoxygenation (Reoxygenation). The transcriptional profiles of relative gene expression values were analyzed using the heatmap 2.0 command of the R language. Red and blue colors represent upregulated and downregulated genes, respectively. The log2 fold change values from pairwise comparison of myc2-2 mutant with WT under air or upon reoxygenation are shown in Supplemental Tables S1 and S2.