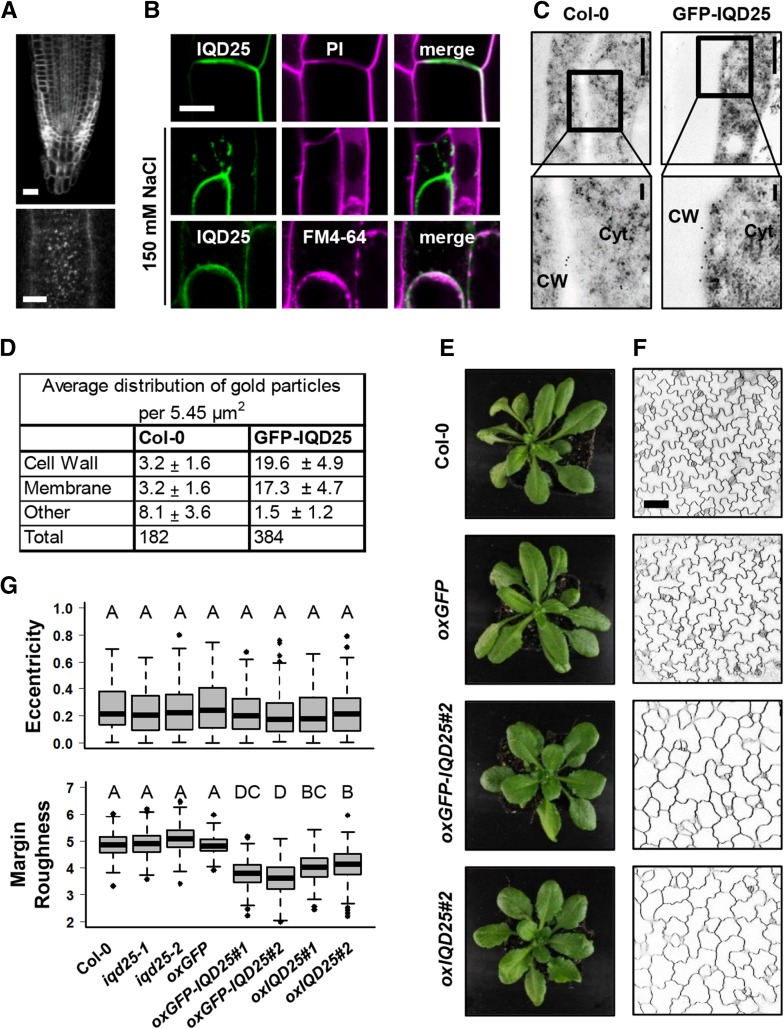
Figure 4.
Subcellular localization and phenotypes in transgenic Pro-35S:GFP-IQD25 Arabidopsis seedlings. A to C, Root cells of 4-d-old transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings expressing GFP-IQD25 under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. A, Subcellular localization of GFP-IQD25 in a primary root tip (top) and surface imaging of root epidermis cells (bottom). Bars = 20 µm (top) and 5 µm (bottom). B, PM localization of GFP-IQD25. GFP-IQD25 localizes to the cell outline, as demonstrated by colocalization with the cell wall dye PI in root cells. After plasmolysis with 150 mm NaCl, GFP-IQD25 fluorescence is detached from PI-stained cell walls and colocalizes with FM4-64-stained PM. C, Localization of GFP-IQD25 by immunogold labeling and transmission electron microscopy. Bottom images are magnifications of the framed regions in the top images. CW, Cell wall; Cyt, cytosol. Bars = 0.5 µm (top) and 0.1 µm (bottom). D, Quantification of gold particles in 10 independent sections. A significant enrichment of gold particles at the PM and cell wall was observed in GFP-IQD25 when compared with the wild-type control (Columbia-0 [Col-0]). E and F, Phenotypes of wild-type, Pro-35S:IQD25, Pro-35S:GFP-IQD25, and Pro-35S:GFP transgenic seedlings. E, Shoots of 4-week-old plants grown on soil under long-day conditions. F, Single optical sections are shown for cotyledon epidermal cells (adaxial side) of 5-d-old seedlings grown under sterile conditions. Cell outlines were visualized with PI. Bar = 50 µm. G, Quantification of cellular elongation (eccentricity) and of the (ir)regularity/(non)smoothness of the cell contour (margin roughness). Results are medians from n ≥ 90 cells and n ≥ 3 seedlings, and boxes range from first to third quartiles. Different letters denote a significant statistical difference. P < 0.005 by one-way ANOVA.