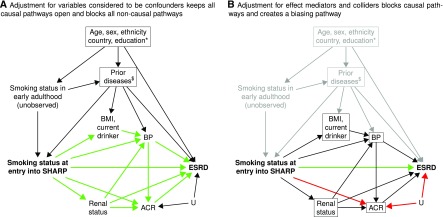
Figure 5.
Causal diagram showing assumed associations between baseline smoking status, ESRD, and baseline characteristics in the Study of Heart and Renal Protection (SHARP). (A) Adjustment for variables considered to be confounders keeps all causal pathways open and blocks all noncausal pathways. (B) Adjustment for effect mediators and colliders blocks causal pathways and creates a biasing pathway. Boxes around variables indicate that they have been adjusted for in analyses. Open causal pathways are highlighted by green arrows (e.g., smoking status at entry into SHARP → urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio [ACR] → ESRD in A), and biasing pathways are indicated by red arrows (e.g., smoking status at entry into SHARP → ACR ← other unknown factors [U] → ESRD in B). *Age, sex, ethnicity, country, and education would also be causes of body mass index (BMI), current drinking, BP, renal status, and ACR. $Prior diseases would also be causes of renal status and ACR.