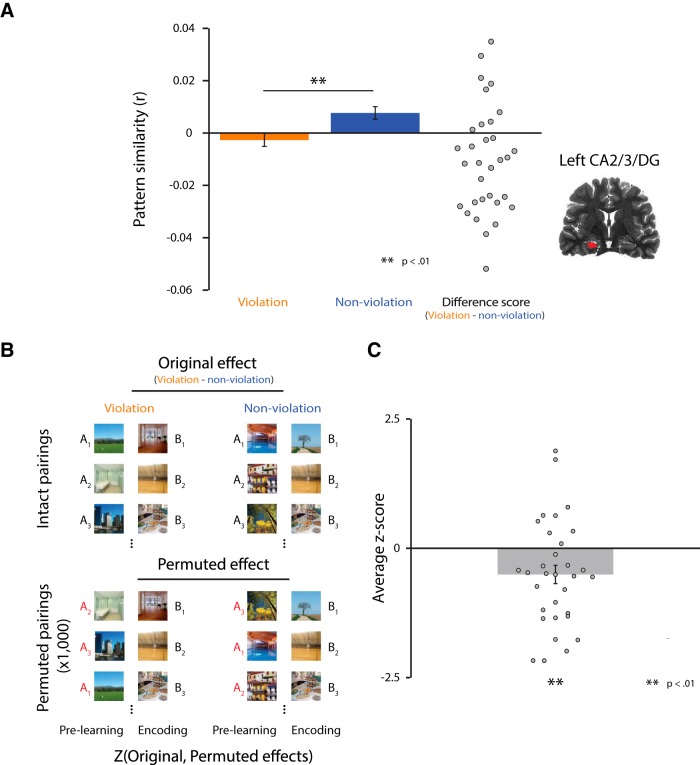
Figure 3.
Neural differentiation effect and item specificity test in left CA2/3/DG. A, Pattern similarity between the prelearning snapshot of A and the postlearning snapshot of B was significantly lower for the violation versus nonviolation conditions. B, Schematic of procedure for randomization analysis. For each participant, we shuffled the AB pairings 1000 times within each condition. In each iteration, we calculated the same prelearning A to postlearning B pattern similarity for each condition and stored the difference between conditions. This produced a null distribution of differences and we calculated the z-score of the original effect with respect to this distribution. The reliability of the z-scores was assessed across participants. C, Original differentiation effect based on the intact AB pairings was reliably lower compared with the null distribution acquired from permuted AB pairings. This result is consistent with the neural differentiation effect being item specific.