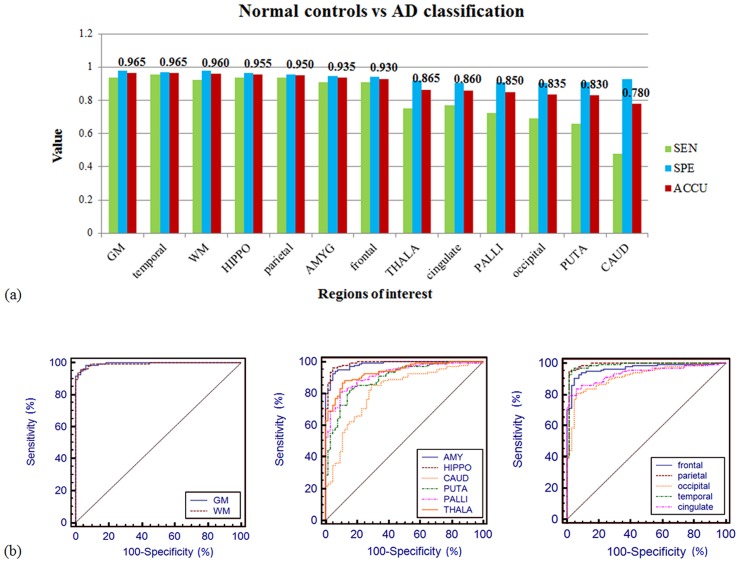
Fig 3.
(a) Classification sensitivity (green), specificity (blue), and accuracy (red) of normal elderly controls versus AD patients with different ROIs. The highest accuracy (96.5%) was achieved using the whole-brain gray matter as ROI with 93.85% sensitivity and 97.78% specificity. The algorithm obtained high sensitivity and specificity (>90%) with half of the ROIs. (b) The ROC curve of the prediction accuracy between normal controls versus AD. The AUCs were larger than 0.98 for the whole-brain gray matter and white matter (left), amygdala and hippocampus (middle), parietal and temporal lobes (right).