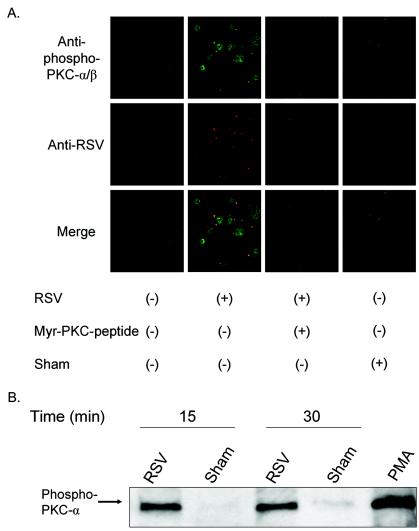
FIG. 7.
Activated PKC-α colocalizes with RSV particles on the cell membrane. (A) Confluent NHBE cells grown on 8-well chamber slides were exposed to RSV at an infectious dose of 20 MOI for 10 min at 37°C following viral binding synchronization for 1 h at 4°C. As negative controls, cells were either pretreated with a PKC-α/β pseudosubstrate inhibitor peptide at 50 μM for 30 min before infection or exposed to a sham treatment (Centricon filtrate obtained from purified RSV). NHBE cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.1% saponin, and stained with rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-Thr-638 PKC-α antibody (green), goat polyclonal anti-RSV antibody (red), and DAPI (blue, nucleus staining). Confocal images (magnification, ×630) were taken by using laser excitation sources for Alexa-488 (green) or Alexa-555 (red) and assembled with Adobe Photoshop software version 7.01. (B) NHBE cells grown in T-25 flasks were infected with purified RSV at an infectious dose of 3 MOI for 15 or 30 min at 37°C following a viral binding synchronization step with incubation at 4°C for 1 h. Membrane fractions of each experimental condition were obtained, equal amounts of protein (8 μg) of the membrane fractions were analyzed by western blot, and the phospho-Thr-638 PKC-α was probed by the specific antibody.