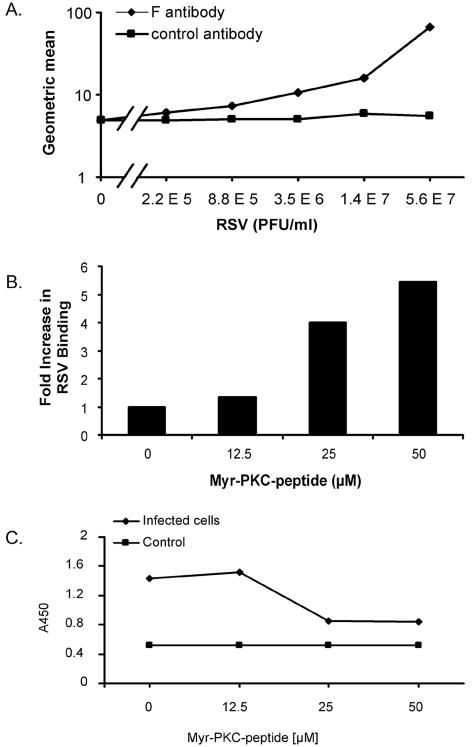
FIG. 9.
Quantitation of viral attachment and penetration. (A) NHBE cells in suspension were incubated on ice with serial fourfold dilutions of RSV to allow viral attachment. After 30 min, cells were washed three times with ice-cold staining buffer, and bound virus was detected with Zenon Alexa-488 anti-RSV F monoclonal antibody. Geometric mean fluorescence values were obtained and graphed. The curve for the isotype control antibody is also shown. (B) A total of 106 NHBE cells per ml in suspension were placed in the absence or presence of different concentrations of the myr-PKC peptide for 30 min at 37°C. Cells were washed with ice-cold basal medium, and 106 cells/ml were exposed to 1.4 × 107 PFU of RSV/ml for 30 min on ice. Unbound virus was removed by washing in ice-cold staining buffer, and bound virus was detected by flow cytometry with Zenon Alexa-488 anti-RSV F monoclonal antibody. (C) NHBE cells grown on 6-well plates were incubated in the absence or presence of different concentrations of the myr-PKC peptide for 30 min before the cells were infected with 1.7 × 106 PFU/well (approximately 5 MOI) for 2 h at 37°C. Cytoplasmic fractions were then isolated from each experimental condition, and a sandwich ELISA was conducted to probe the presence of RSV N protein in these fractions. TMB substrate was then added, and the plate was read at 450 nm (A450). The cytoplasmic fractions of noninfected cells were used as a control. These assays were duplicated with similar results.