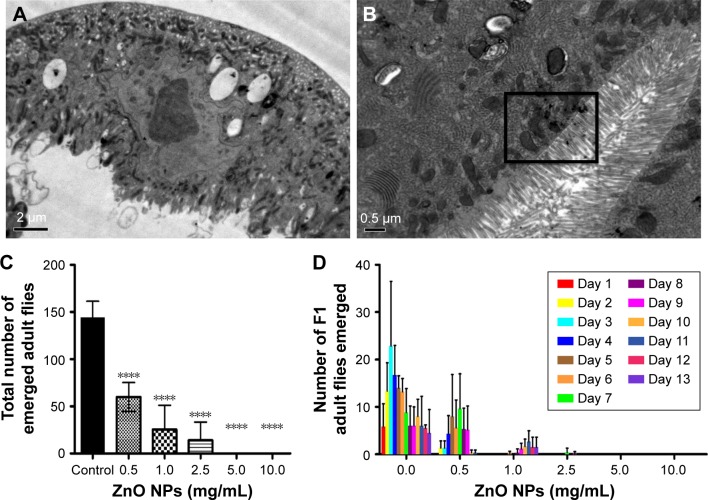
Figure 6.
ZnO NPs adversely affect the viability of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster.
Notes: (A) EM imaging of the intestinal lumen control larva. (B) EM imaging on larval uptake of ZnO NPs at the intestinal lumen. Presence of ZnO NPs is indicated by the boxed area. (C) Treatment of wild-type flies with ZnO NPs results in a significant decrease in viability. Wild-type flies fed with different doses of ZnO NPs were removed after 5 days upon ingestion of ZnO NPs. Successfully, enclosed F1 adult flies were counted and their survival rate was presented after following up for 9 days. ****P<0.0001. (D) Treatment of wild-type flies with ZnO NPs results in a delay in development. Error bars = standard error of mean.
Abbreviations: EM, electron microscope; NPs, nanoparticles.