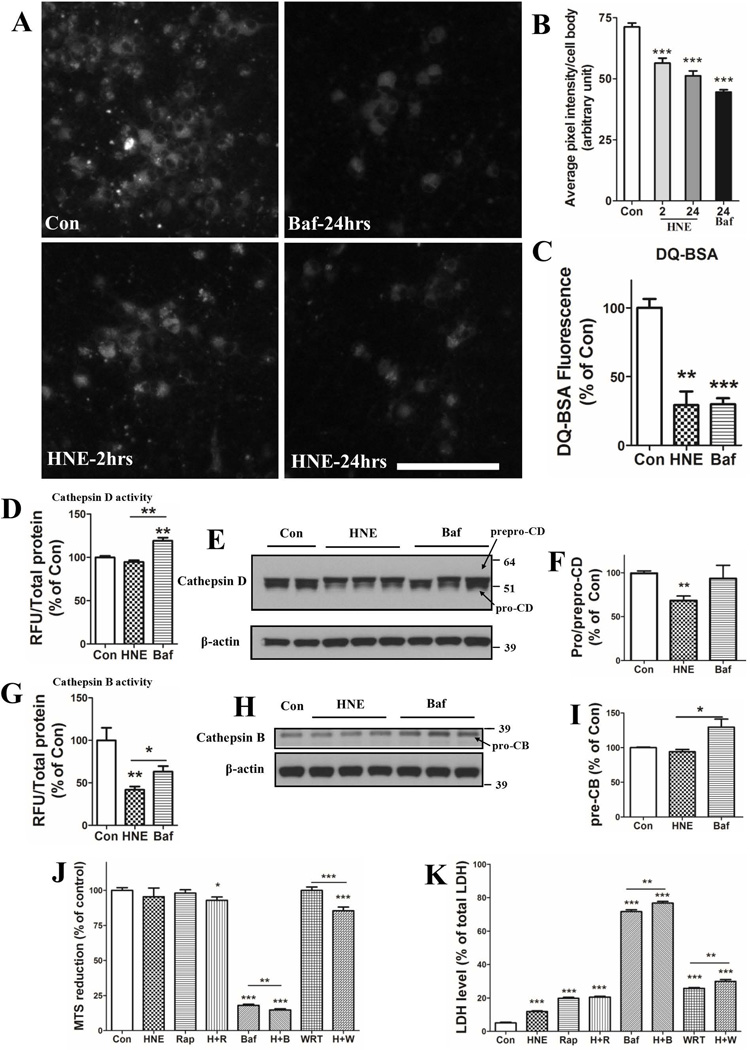
Figure 6.
HNE impairs lysosomal function. (A and B) Neurons were first treated with 0.05% ethanol (Con) or 100 nM bafilomycin (Baf) for 24 hours, or with 5 µM HNE for 2 and 24 hours, then incubated in the presence of LysoSensor green for 5 minutes and images of LysoSensor fluorescence were acquired. Representative images of LysoSensor fluorescence are shown in panel A and results of quantification of average fluorescence pixel intensity per cell body are shown in panel B (values are the mean and SEM of measurements made on 25 – 35 neurons in 3 separate cultures for each condition. Scale bar in panel A = 100 µm. (C) Neurons plated in black-walled 96-well plates were treated for 6 hours with 0.05% ethanol (Con) 5 µM HNE or 100 nM bafilomycin A (Baf) and then subjected to the DQ-BSA protocol; fluorescence intensities were quantified using a plate reader. (D – I) Neurons were treated for 6 hours with 0.05% ethanol (Con) 5 µM HNE or 100 nM bafilomycin A (Baf) and then enzymatic activities (D and G) and protein levels (E, F, H and I) of cathepsins B and D were measured. Values are the mean and SEM of determinations made in 3 separate experiments. (J and K) Neurons were exposed to the indicated individual or combined treatments for 24 hours and neuronal viability was evaluated by MTS (J) and LDH release (K) assays. HNE, 10 µM; Rap: 100 nM rapamycin; Baf, 100 nM bafilomycin A; WRT, 5 µM wortmannin. Values are the mean and SEM of determinations made in 3 independent experiments. Differences among groups were analyzed by Student’s t-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared to the control value or to the adjacent treatment condition as indicated.