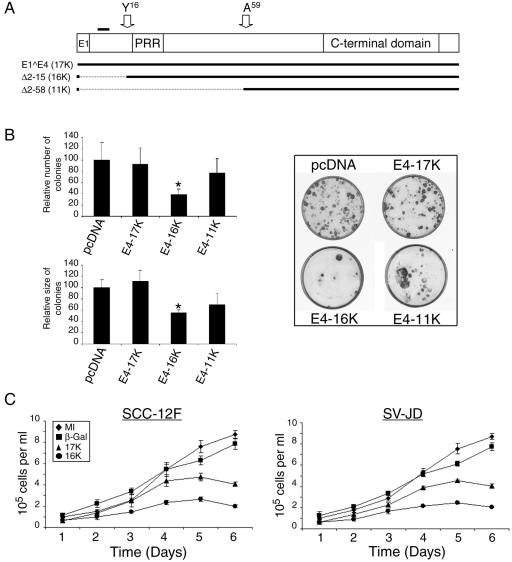
FIG. 2.
Expression of HPV1 E4 represses keratinocyte growth. (A) The structure of the full-length HPV1 E1∧E4 protein. E1, the small exon derived from the E1 ORF; PRR, the proline-rich region; C-terminal domain, a conserved domain necessary for E4 oligomerization (2, 33). The position of the leucine-rich motif 10LLGLL14 that is required for colocalization with the keratin intermediate filaments (33) is indicated by a bold line above the diagram, and the positions of the N termini of the proteolytically cleaved products of 16 kDa and 10 or 11 kDa (33) are indicated with arrows. The structure of the two mutant proteins Δ2-15 (E4-16K) and Δ 2-58 (E4-11K) is shown below. (B) Graphical representation of the relative number and size (diameter) of clones produced following transfection of SCC-12F cells with the different HPV1 E4-containing plasmids, relative to the empty pcDNA3.1 vector (left). Data are shown as means ± standard deviations, and the asterisk indicates a statistical significance of 99.9%. Examples of SCC-12F cells transfected with empty vector or the corresponding HPV1 E4-containing plasmids are shown on the right side of the panel. (C) Short-term growth profiles, performed in triplicate, of SCC-12F and SV-JD keratinocytes infected with the different rAds. MI, mock-infected.