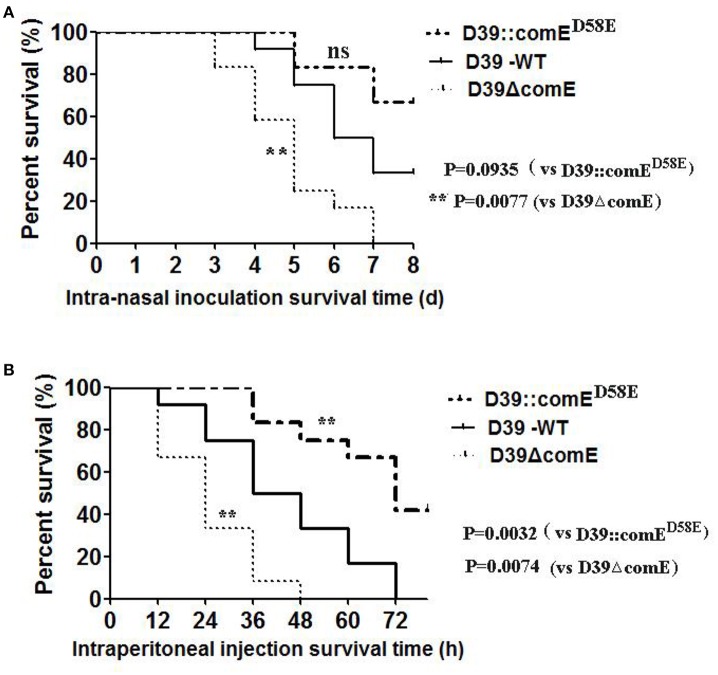
Figure 7.
The role of ComE in the virulence of S. pneumoniae. (A) Survival of mice during pneumococcal lung infection. Groups of Balb/c mice (n = 12) were challenged intranasally with D39-WT, D39ΔcomE and D39::comED58E mutant using 7.5 × 107 CFU of bacteria. Mice were subsequently monitored for 8 days, and survival was recorded every day. D3-WT vs. D39ΔcomE, **p = 0.0077; D39-WT vs. D39::comED58E, no significant difference, p = 0.0935). (B) Survival of mice during pneumococcal bacteremia. Groups of Balb/c mice (n = 12) were administered with D39-WT, D39ΔcomE and D39::comED58E mutant by intraperitoneal injection using 7.5 × 102 CFU of bacteria. Mice were subsequently monitored for 78 h, and survival was recorded every 12 h. D39-WT vs. D39ΔcomE, **p = 0.0074; D39 WT vs. D39::comED58E, **p = 0.0032).