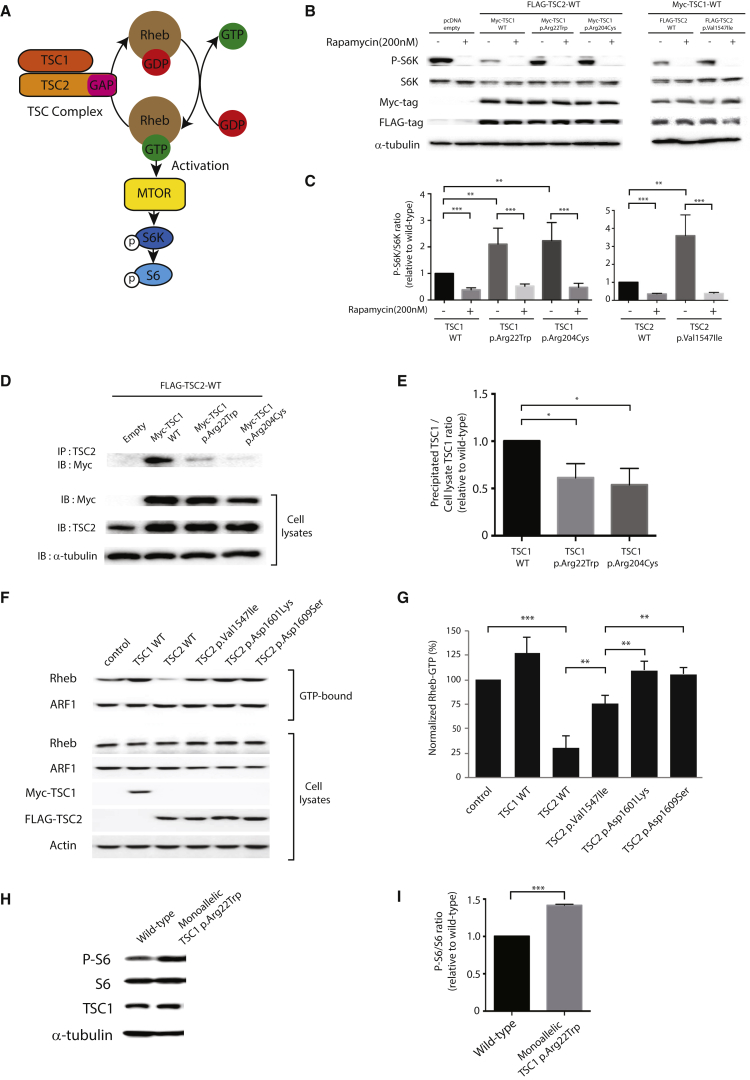
Figure 2.
The Identified Mutations Induce Hyperactivation of the mTOR Pathway by Disrupting the Formation or Function of the TSC1-TSC2 Complex
(A) Schematic figure showing that mTOR kinase activation is regulated by the GAP domain of the TSC complex through hydrolysis of GTP-bound Rheb.
(B) Immunoblot analysis of S6K phosphorylation in TSC1 or TSC2 mutant HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type TSC1 and the indicated TSC1 mutants or with FLAG-tagged wild-type TSC2 and the indicated TSC2 mutant and then treated with rapamycin (200 nM) for 1 hr. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. WT, wild-type.
(C) Quantification of the blotting intensity. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3–5 per group). ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with the wild-type (Student’s t test).
(D) Immunoprecipitation assay of mutant TSC1 and wild-type TSC2. HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type or mutant TSC1 and FLAG-tagged wild-type TSC2. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-TSC2 antibody and subsequently immunoblotted with anti-Myc antibody. Immunoprecipitation assays of mutant TSC2 and wild-type TSC1 are presented in Figure S5.
(E) Quantification of the TSC1 blotting intensity immunoprecipitated with TSC2 antibody. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 4 per group). ∗p < 0.05 compared with the wild-type (Student’s t test).
(F) GTP-agarose bead pull-down assay for Rheb in mutant TSC2-expressing cells. HEK293 cells were transfected or co-transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type TSC1, FLAG-tagged wild-type TSC2, or TSC2 p.Val1547Ile. Cell lysates were incubated with GTP-agarose beads, and the GTP-bound materials were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Rheb or anti-ARF1 antibodies. Total cell lysates were also immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
(G) Quantification of the GTP-bound Rheb blotting intensity. Two point substitutions (TSC2 p.Asn1601Lys and p.Asn1609Ser) have been reported to abolish TSC2 GAP activity and thus were used as the enzyme-dead control. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3 per group). ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student’s t test).
(H) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated S6 (P-S6), S6, and Tsc1 in Neuro2A cells carrying monoallelic TSC1 p.Arg22Trp. The level of phosphorylated S6 was significantly increased in the stable cell line with monoallelic TSC1 p.Arg22Trp, indicating that the mTOR pathway was hyperactivated by the heterozygous monoallelic mutation. The level of TSC1 was unaffected by the mutation.
(I) Quantification of the blotting intensity of S6 phosphorylation. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3 per group). ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with the wild-type (Student’s t test). Cells were harvested without serum starvation for lysate extraction in all experiments.