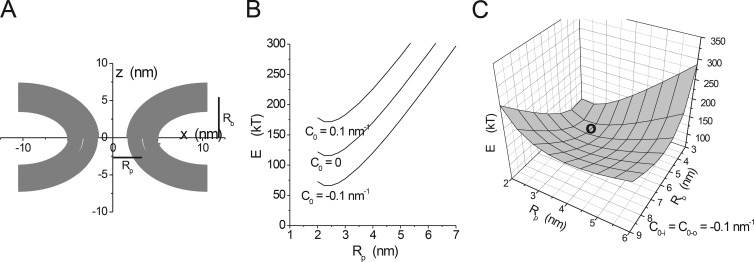
Figure 6.
Minimum energy fusion pores. (A) The fusion pore is a surface of revolution around the z axis formed by a lipid bilayer. This shape was obtained by minimizing the mean curvature of two parallel lipid monolayers subject to the constraint of a pore radius Rp = 3.3 nm and a bilayer separation of twice Rb = 5.45 nm (note that these are distances to the center of the bilayer; further note that this minimization omitted the possibility of an inflection that can introduce a bowing shape that reduces the energy further; Yoo et al., 2013). (B) Minimum energies determined for Rb = 3 nm and varied Rp. This plot shows a stable minimum at Rp = ∼2.5 nm. The spontaneous curvature of the lipid (C0) has a major influence on the energy but not on the position of the minimum. (C) Varying both Rp and Rb reveals a global minimum at the location indicated by the circle, at Rp = 2.75 nm and Rb = 4.2 nm (modified from Jackson [2009] with permission from Springer).