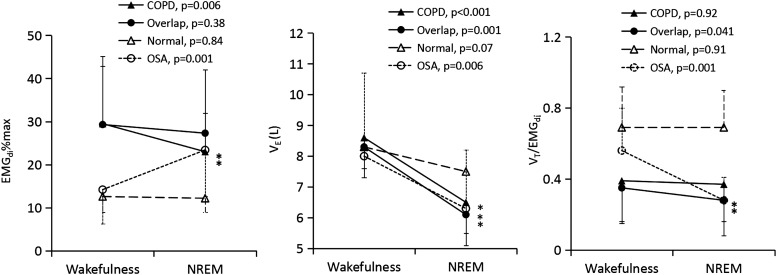
Figure 2.
Electromyogram (EMG)di% (left panel), ventilation (middle panel) and the VT/EMGdi (right panel) in patients with COPD alone, overlap syndrome, normal subjects and patients with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA). Ventilation decreases from wakefulness to sleep in all four groups but only in patients with COPD, overlap syndrome and OSA is the reduction statistically significant. EMGdi decreases in patients with COPD alone but increases in patients with OSA from wakefulness to non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, whereas it remains the same in normal subjects and patients with overlap syndrome. VT/EMGdi decreases from wakefulness to sleep in patients with overlap syndrome and those with OSA but it changes little in normal subjects and patients with COPD alone. The decrease in ventilation is associated with a reduction of EMGdi in patients with COPD alone whereas ventilation reduction is associated with decreased VT/EMGdi in patients with overlap syndrome and those with OSA.