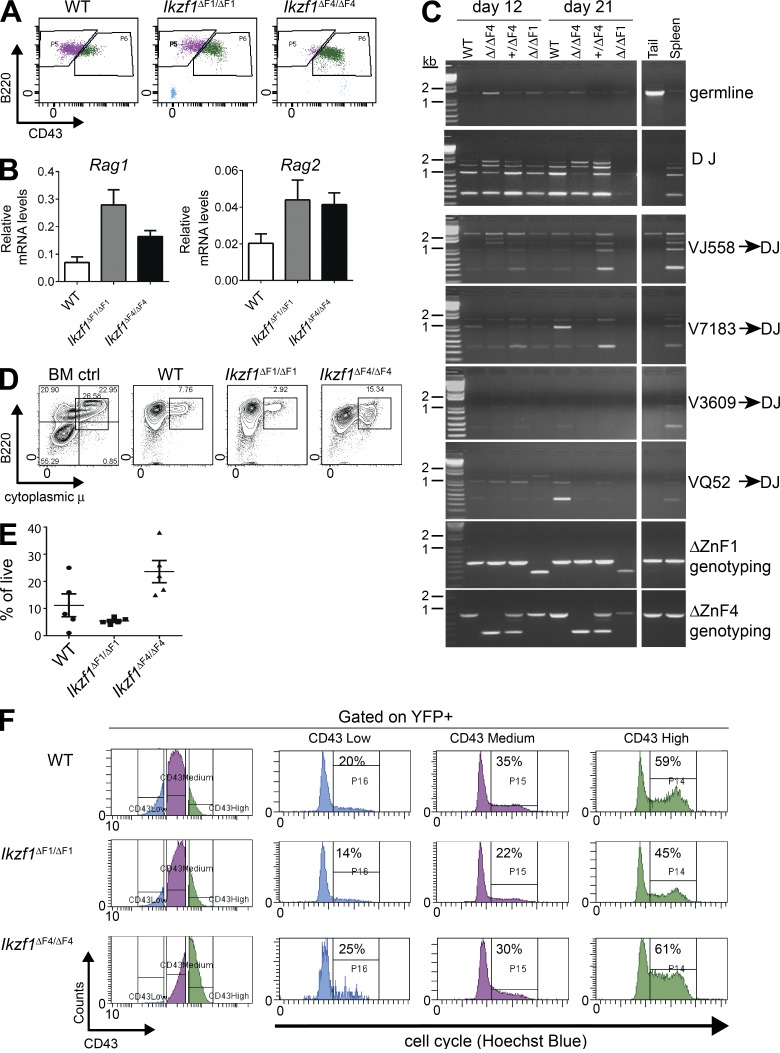
Figure 2.
Ikzf1ΔF4/ΔF4mutant BCR-ABL1+ cells display immature cell surface phenotype but undergo successful IgH V(D)J recombination, and increased cell cycle correlates with CD43 expression. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of CD43 on in vitro grown BCR-ABL1–transformed WT, Ikzf1ΔF1/ΔF1, and Ikzf1ΔF4/ΔF4 pre–B ALL cells. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Rag1 and Rag2 mRNA expression on in vitro grown BCR-ABL1–transformed WT, Ikzf1ΔF1/ΔF1, and Ikzf1ΔF4/ΔF4 pre–B ALL cells. UBC was used as a reference gene. (C) IgH V(D)J recombination was analyzed by PCR (Schlissel et al., 1991) with genomic DNA from BCR-ABL1–transformed WT, Ikzf1ΔF1/ΔF1, and Ikzf1ΔF4/ΔF4 cells, and genomic DNA from WT tail and spleen was used as negative and positive controls, respectively. (D and E) Expression of cytoplasmic μ chain was analyzed by flow cytometry. Whole mouse BM was used as positive control. One representative is shown in (D) and results from multiple samples analyzed in independent experiments are summarized in E as fraction of cells expressing cytoplasmic μ (% of live; E). (F) Flow cytometry analysis of CD43 and cell cycle analysis on in vitro cultures of BCR-ABL1–transformed WT, Ikzf1ΔF1/ΔF1, and Ikzf1ΔF4/ΔF4 cells (gated on YFP+), displaying cell cycle activity of cells gated on low, medium, or high expression of CD43, respectively. All results are reproduced in two or more independent experiments.