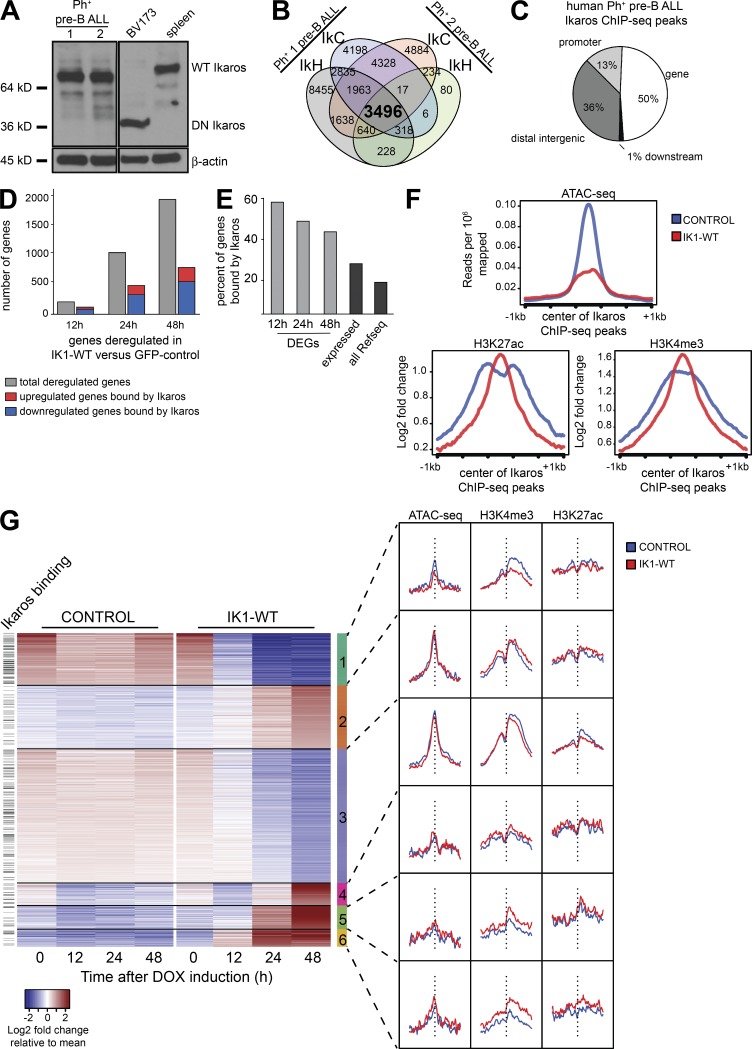
Figure 5.
Genome-wide analysis of Ikaros binding and Ikaros-induced changes in chromatin in human BCR-ABL1+ pre–B ALL. (A) Western blot analysis of extracts from two in vitro growing patient-derived xenograft-expanded Ph+ pre–B ALL cells that express WT Ikaros and that were used for Ikaros ChIP-Seq. Also shown are the controls from BV173 cells and mouse spleen cells that express the DN IK6 isoform and full-length WT Ikaros, respectively. (B) Analysis of Ikaros ChIP-Seq datasets from two patient-derived BCR-ABL1+ pre–B ALL samples (Fig. S2). (C) Genome-wide distribution of human Ph+ pre–B ALL ChIP-Seq peaks in relation to RefSeq genes. (D) Total number of deregulated genes and the proportion with annotated Ikaros ChIP-Seq binding at each time point. (E) The percentage of differentially expressed genes (DEG) with an Ikarospeak within 100 kb in each comparison (12, 24, or 48 h IK1-WT versus GFP (control); FDR < 0.005; fold change > 2) was determined (light gray). The percentage of expressed genes bound by Ikaros was determined by defining all genes with an Ikaros peak having a mean of the regularized log value > 1 across all RNA-Seq samples. The percentage of all genes bound by Ikaros was determined by dividing the unique Ikaros bound genes by the total 50,801 RefSeq genes in the ChIP BETA database (Wang et al., 2013). (F) Analysis of chromatin accessibility by ATAC-Seq and histone modification ChIP-Seq in WT Ikaros-induced and control human pre–B ALL cells relative to Ikaros-enriched regions (G) Heat map based on k-means clustering of normalized log transformed read counts of differentially expressed genes in GFP-sorted cells after IK1-WT induction compared with control after a period of 48 h after induction. The signal from IK1-WT and control samples for ATAC-Seq and ChIP-Seq are shown for each cluster on the right. The vertical dashed line represents the center of the TSS of each gene, and the genes with an Ikarospeak within 10 kb of the TSS are shown on the left.