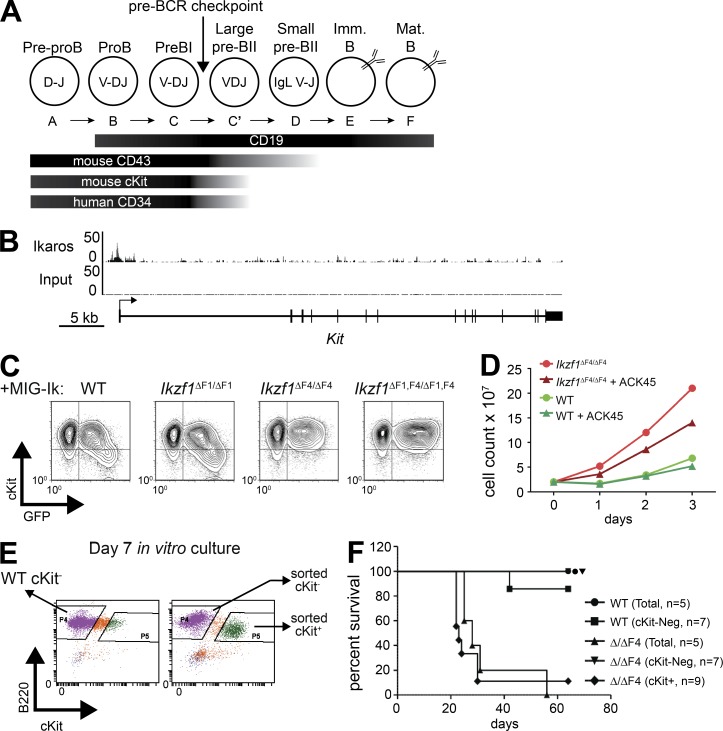
Figure 6.
Kit is a ZnF4-dependent Ikaros target gene that confers growth advantage and correlates with aggressive leukemia. (A) Schematic diagram of relevant cell surface markers expressed on developing B cells. (B) ChIP-seq tracks of Ikaros and input from mouse pro-B cells (Bossen et al., 2015) demonstrates binding of Ikaros at the Kit promoter. (C) Retroviral overexpression of Ikaros isoforms containing different subsets of the DNA-binding zinc fingers (IRES-GFP) in Ikzf1null, EBF1-rescued noncommitted pro–B cells (Reynaud et al., 2008). GFP and c-Kit expression was analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Mouse pre–B ALL cells from WT and Ikzf1ΔF4/ΔF4 mutant mice were created and cultured as described in Fig. 1 A. Cell growth with and without c-Kit blocking Ab (ACK45; 10 µg/ml) was measured by daily cell count. (C and D) One representative of two independent experiments. (E) Day 7 cultures of mouse pre–B ALL cells from WT and Ikzf1ΔF4/ΔF4 mutant mice were sorted as indicated based on c-Kit expression. (F) Sorted cells from E or bulk unsorted day 7 cultures were i.v. injected into nonirradiated, immunocompetent WT C57BL/6 mice. Mice were monitored and euthanized upon development of leukemia. Leukemia was confirmed by necropsy and flow cytometry analysis, and survival of indicated cohorts is represented by Kaplan-Meyer curve.