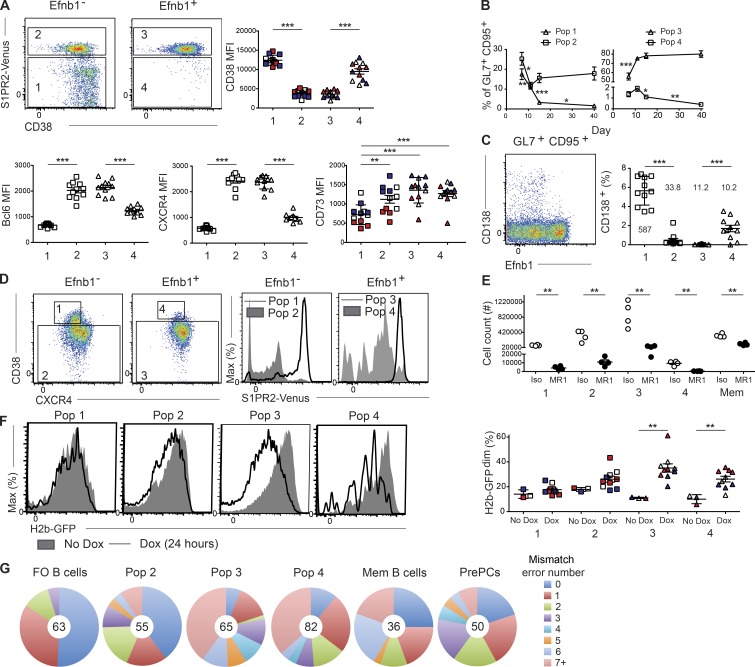
Figure 3.
Ephrin-B1 and S1pr2 can distinguish transitional populations of GC B cells. (A) Representative plots (left) of S1pr2 (as defined using S1pr2Venus/+ mice) and CD38 expression in splenic Efnb1– and Efnb1+ IgDloGL7+CD95+ B cells. Expression of CD38 (right), Bcl6, CXCR4, and CD73 (bottom) was determined at day 7 (red), 11 (white), or 15 (dark blue) after LCMV Arm infection in Efnb1– S1pr2lo (Pop 1), Efnb1– S1pr2hi (Pop 2), Efnb1+ S1pr2hi (Pop 3), and Efnb1+ S1pr2lo (Pop 4) IgDloGL7+CD95+ B cells. Data for the Bcl6 and CXCR4 plots are pooled from three experiments with three to four mice per group at day 11 after infection. (B) Percentage of IgDloGL7+CD95+ B cells that comprise the populations defined in A at day 7, 11, 15, and 40 after LCMV Arm infection. Data for the CD38 and CD73 plots are from one experiment with three to four mice per time point at days 7, 11, and 15 and are representative of two independent experiments for days 7 and 15, one experiment with four mice at day 40, and four experiments at day 11. (C) Representative plot (left) of CD138 and Ephrin-B1 expression in splenic B220+ IgDloGL7+CD95+ B cells. Percentage of CD138+ cells within each population as defined in A (right). Number indicates the mean number of CD138+ cells in each population per million B cells. Data are pooled from three experiments with three to four mice per group at day 11 after infection. (D) Representative plots (left) of IgDloGL7+CD95+ GC B cells are divided into four subsets (labeled 1–4) with the following marker profile: Efnb1– CD38+CXCR4lo (Pop 1), Efnb1– CD38– (Pop 2), Efnb1+ CD38– (Pop 3), and Efnb1+ CD38+CXCR4lo (Pop 4; left). Representative plots (right) of S1pr2 (as defined using S1pr2Venus/+ mice) in the populations defined using CD38 and CXCR4. (E) Number of Efnb1– CD38+CXCR4lo (Pop 1), Efnb1– CD38– (Pop 2), Efnb1+ CD38– (Pop 3), and Efnb1+ CD38+CXCR4lo (Pop 4) IgDloGL7+CD95+ B cells and memory (IgDloGL7–CD95+CD73+) B cells at day 13 after LCMV Arm infection in mice treated with anti-CD40L (MR1) or an isotype control antibody from days 9–12. Data are from one experiment representative of two independent experiments with four mice per group. (F) Representative histograms (left) of H2b-GFP expression in the populations defined in D in untreated or doxycycline treated Tet-off H2b-GFP mice. Analysis (right) of the percentage of H2b-GFPdim at day 7 (red), day 11 (white), or day 15 (dark blue) after LCMV Arm infection. Mice were treated with doxycycline (dox) 24 h before analysis with one mouse per time point not treated to determine background GFP dilution. Data are from one experiment representative of two independent experiments with three to four mice per time point. (G) Analysis of mismatch error rate frequency in 700 bp of the JH558 intronic sequence in follicular (IgD+GL7–) B cells, Efnb1– S1pr2hi (Pop 2), Efnb1+ S1pr2hi (Pop 3), Efnb1+ S1pr2lo (Pop 4) IgDloGL7+CD95+ B cells, memory (IgDloGL7–CD95+CD73+) B cells, and pre plasma (IgDloGL7+CD95+CD138+) cells sorted at day 11 after LCMV infection. Number of sequences analyzed for each population is listed in the center of each circle. Cells were pooled from two independent experiments with four mice per experiment. Statistical analyses were performed using the unpaired two-tailed Student's t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).