FIGURE 5.
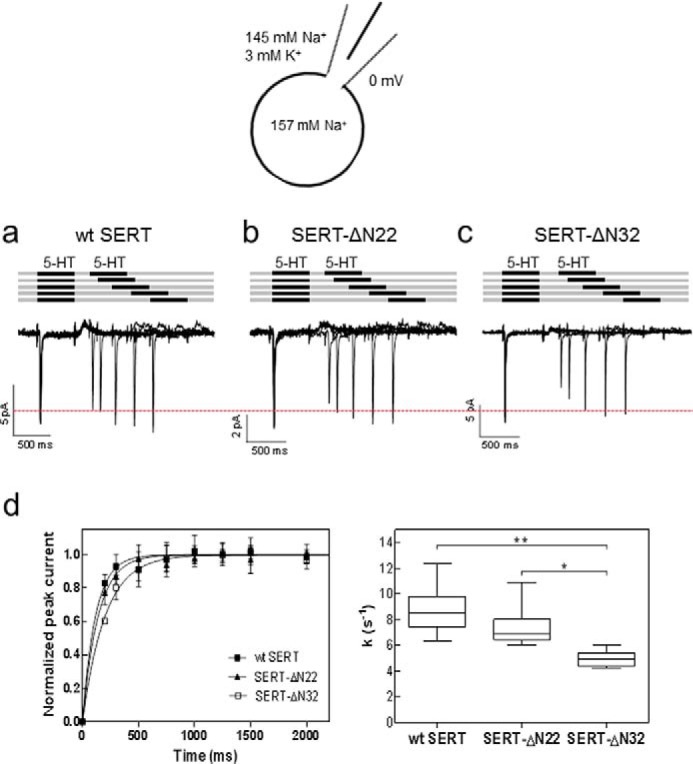
Substrate-induced peak currents elicited by paired pulse applications of serotonin to HEK293 cells expressing wild type SERT (a), SERT-ΔN22 (b), and SERT-ΔN32 (c) in the presence of high internal Na+. a–c, peak current recovery protocol and representative traces. 5-HT (10 μm) was applied for 0.5 s followed by variable (increasing) washout intervals and subsequent 5-HT test pulses. The presence of high internal Na+ precludes progression through the transport cycle, thus resulting in the suppression of the steady state current (Fig. 4, a–c) and forces SERT into the exchange mode. The recovery of the peak current (elicited by the second 5-HT pulse) therefore monitors the fraction of transporters that have completed the half-cycle to return to the outward facing conformation and are available for renewed binding of serotonin. d, the time course of peak current recovery was plotted for wild type SERT (closed squares), SERT-ΔN22 (closed triangles), and SERT-ΔN32 (open squares) and fitted to a monoexponential function. Data are means ± S.D. (error bars) from six independent experiments. The box plot shows the median recovery rates (k) and the interquartile range extracted from the individual monoexponential recovery curves; whiskers show maximum and minimum values. The recovery rate for SERT-ΔN32 was significantly lower (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
