FIGURE 1.
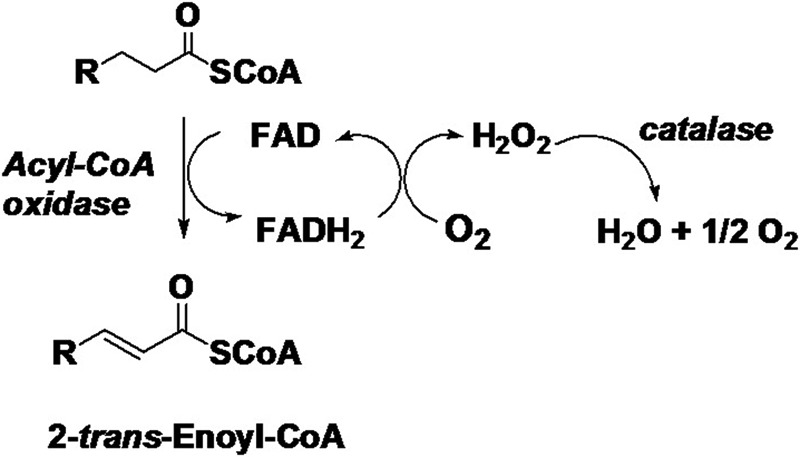
Reaction catalyzed by acyl-CoA oxidase. In the reductive half-reaction, the substrate acyl-CoA is α,β-dehydrogenated into the corresponding 2-trans-enoyl-CoA, with electrons transferred to FAD, which becomes reduced, whereas in the oxidative half-reaction reduced FAD is reoxidized by molecular oxygen, generating hydrogen peroxide.
