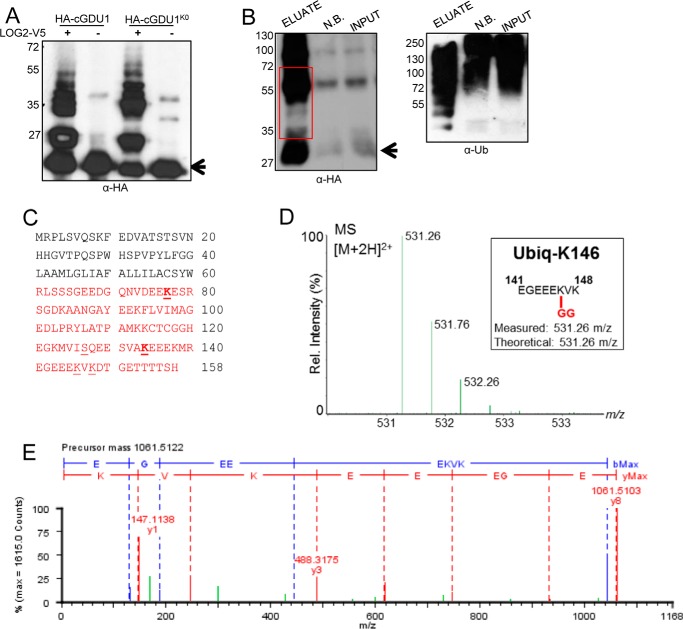
FIGURE 4.
GDU1 is ubiquitinated at lysines in vitro and in planta. A, in vitro ubiquitination of HA-cGDU1-His6 (wild-type or the K0 mutant lacking all cytosolic lysines) by V5-tagged LOG2. − lanes contain all ubiquitination assay components except LOG2. B, nickel-NTA affinity purification of His6-HA3-GDU1 from transiently transformed N. benthamiana leaves co-infiltrated with LOG2-HA. Input, cell-free supernatant after tissue lysis. NB, not bound (protein that did not bind nickel beads). Eluate, protein eluted from nickel-NTA beads with 350 mm imidazole and heat. The red box in B refers to the region on the corresponding SDS-polyacrylamide gels subjected to in-gel trypsinization and subsequent electrospray ionization-MS/MS tandem mass spectrometry to identify ubiquitination sites. Arrows in A and B denote un-modified HA-cGDU1-His6 and His6-HA3-GDU1, respectively. Numbers to the left of Western blots indicate protein mass in kDa. C, GDU1 amino acid sequence with mass spectrometry-identified ubiquitination sites indicated with underlines (identified in in vitro assays only) or bold underlines (identified in both in vitro and in planta assays). Red text demarcates the cGDU1 region in the GDU1 protein sequence. Serine 127 (underlined) was identified as the sole in vitro ubiquitination site in HA-cGDU1K0-His6. D and E, mass spectra for the parent ion (D) and MS/MS fragmentation (E) indicating in vitro ubiquitination of Lys-148 (ubiquitinated peptides in green).