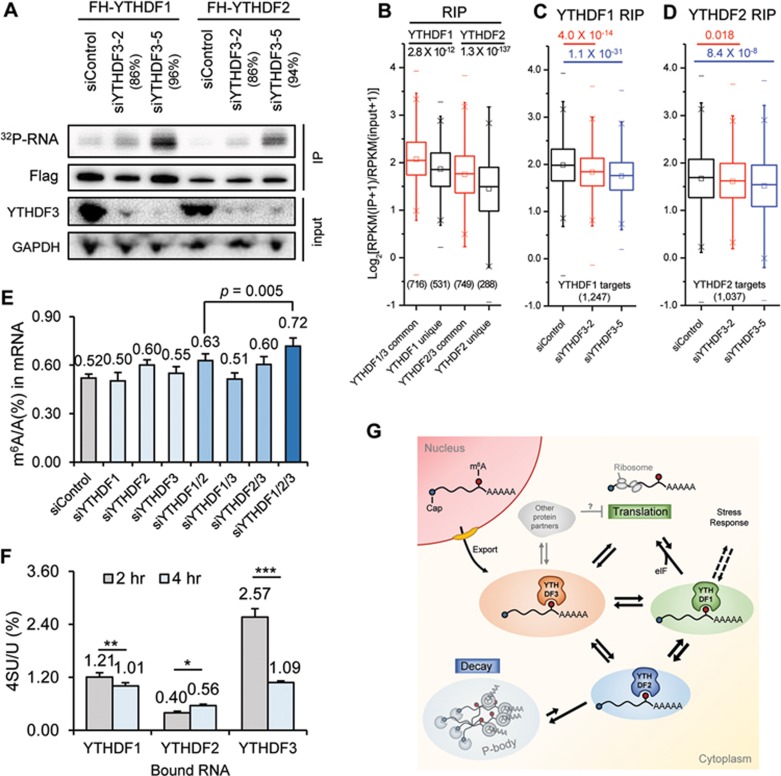
Figure 4.
YTHDF proteins form an interconnected network in the cytosol. (A) Total RNAs bound by YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 quantified with PAR-CLIP followed by 5′-32P labelling in the control HeLa cells and cells depleted of YTHDF3 using two different siYTHDF3 oligos. Knockdown efficiency of the two siYTHDF3 oligoes was indicated, respectively. Samples loaded in the radioactivity gel were normalized with immunostaining of the Flag-tagged protein. (B-D) Genome-wide analysis of target affinity of YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 with or without YTHDF3. Box plot of RIP enrichment of different groups of YTHDF targets in siControl samples (B), and that of YTHDF1 targets (C) or of YTHDF2 targets (D) in siControl and siYTHDF3 samples. Box, 25%-75%; “−”, max and min; “×”, 1% and 99%; “□”, median. P values were calculated from a two-sided Mann-Whitney test. (E) LC-MS/MS quantification of m6A levels of HeLa cells treated with siControl, siYTHDF1, siYTHDF2, siYTHDF3, and combinations of those oligoes. Error bars, mean ± sd, n = 4 (two biological replicates × two technical replicates). (F) LC-MS/MS quantification of 4SU (4-thio-uridine) level in mRNAs pulled down with YTHDF1-3 2-hour and 4-hour post a 1-hour 4SU labeling of nascent RNAs. Error bars, mean ± sd, n = 3∼4. P values were calculated using paired two-sided Student's t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005; (G) A proposed model for an integrated partition network for m6A-modified transcripts mediated by YTHDFs in the cytosol. While YTHDF1 functions in translation regulation and YTHDF2 dominates in accelerating mRNA decay, YTHDF3 could serve as a hub for fine-tuning the RNA accessibility of YTHDF1-2. These three mRNA pools controlled by YTHDF1-3 could be interchangeable and highly dynamic, resulting in an interconnected and dynamic mRNA modulation through m6A. YTHDF3 might also interact with other protein partners (grey) to negatively impact translation.