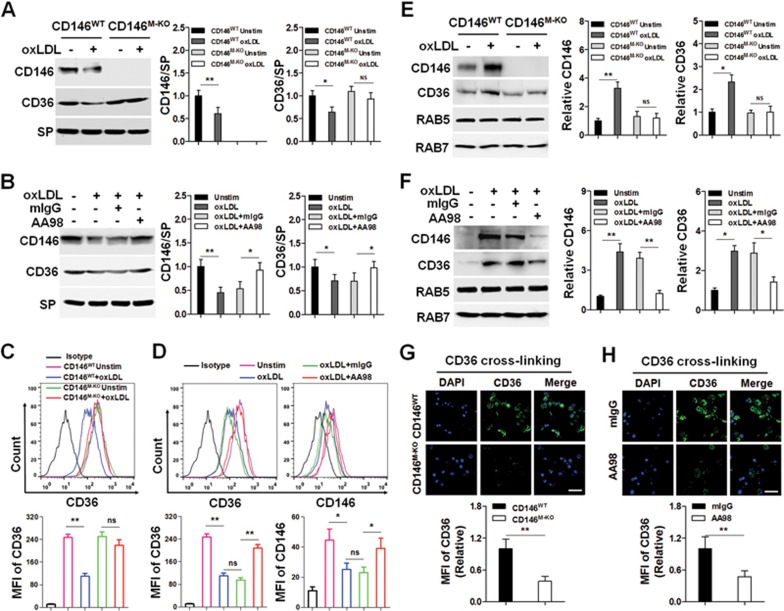
Figure 5.
CD146 facilitates CD36 internalization. Western blot (A, B) and FACS analysis (C, D) of membrane CD146 and CD36 in oxLDL-stimulated BMDMs isolated from CD146WT or CD146M-KO mice (A, C) or BMDMs with or without pretreatment with anti-CD146 AA98 (50 μg/ml) (B, D). Membrane fractions were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. SP (sodium pump) served as a loading control for membrane fractions. Right panel: quantification of CD36 or CD146 levels relative to SP (A, B). Bottom panel: quantification of the MFI of CD36 or CD146 (C, D). (E, F) Western blots of CD146 and CD36 in endosomal fractions of BMDMs isolated from CD146WT or CD146M-KO mice (E) or BMDMs with or without pretreatment with anti-CD146 AA98 (50 μg/ml) (F). Endosomal fractions were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Right panel: quantification of CD36 or CD146. (G, H) BMDMs from CD146WT or CD146M-KO mice or BMDMs with or without pretreatment with AA98 (50 μg/ml) were labeled with a CD36-cross-linking antibody. Then, the cells were incubated at 37 °C to cross-link CD36. The cells were then washed with cold acid wash buffer to deplete surface CD36. Confocal microscopy was used to detect and quantify CD36 internalization. Bottom panel: quantification of the MFI of CD36. *P < 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001. The data represent three independent experiments.