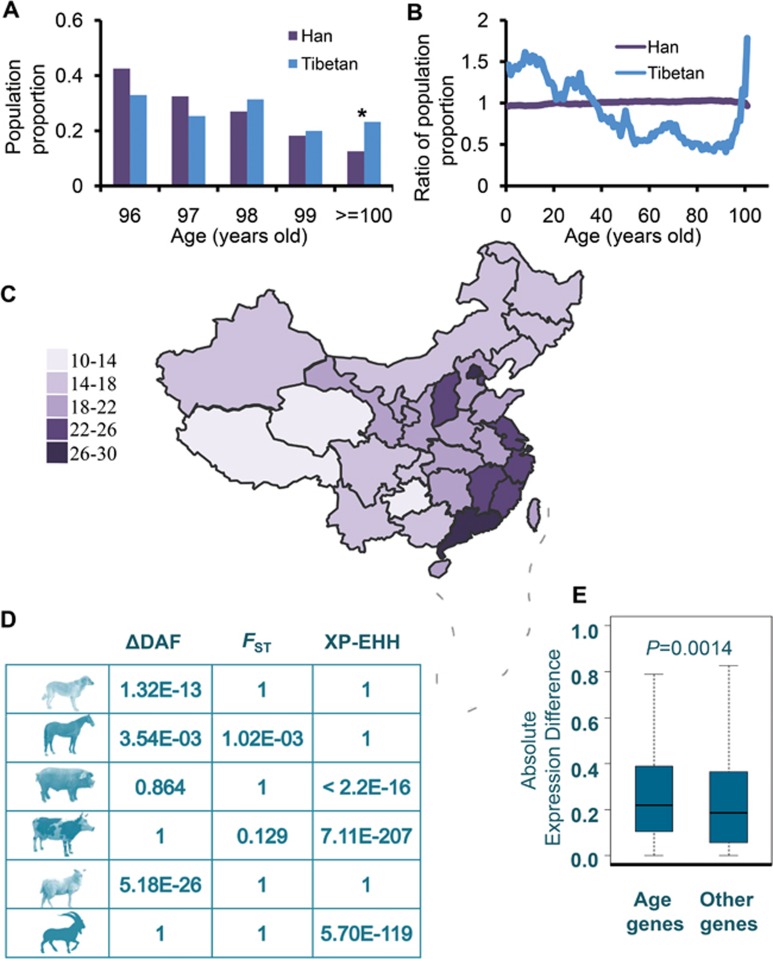
Figure 1.
Analysis of the age composition of Tibetans, and rapid evolution and differential expression of genes associated with aging. (A) Proportion of the population (×10−4) with male individuals > 95 years of age, Han and Tibetans. *P = 1.23E-07. (B) Ratio of the population proportion computed as the proportion of Tibetan or Han population divided by the proportion for the whole Chinese population for different ages. (C) Heatmap of RPDO across China. The relative proportion of deaths in the old population (ab. RPDO) (≥ 60 years old) was defined as the proportion of deaths in old population (≥ 60 years old) divided by the proportion of deaths in the other population (< 60 years). Data for Taiwan are not available. (D) Significantly higher values of ΔDAF, FST and XP-EHH for SNPs in genes associated with aging versus SNPs in other genes. P-values according to Mann-Whitney U-test are presented. (E) Higher level of gene expression difference was found for aging-related genes than for other genes. FPKM, as expression value, was calculated by Cufflinks for each gene15. Expression difference for each gene was calculated by the absolute difference of log2 (FPKM+1) values of the gene in lungs of Tibetan and Min pigs.