Figure 2. Influence of expression level on ampicillin resistance and wild-type/mutant discrimination.
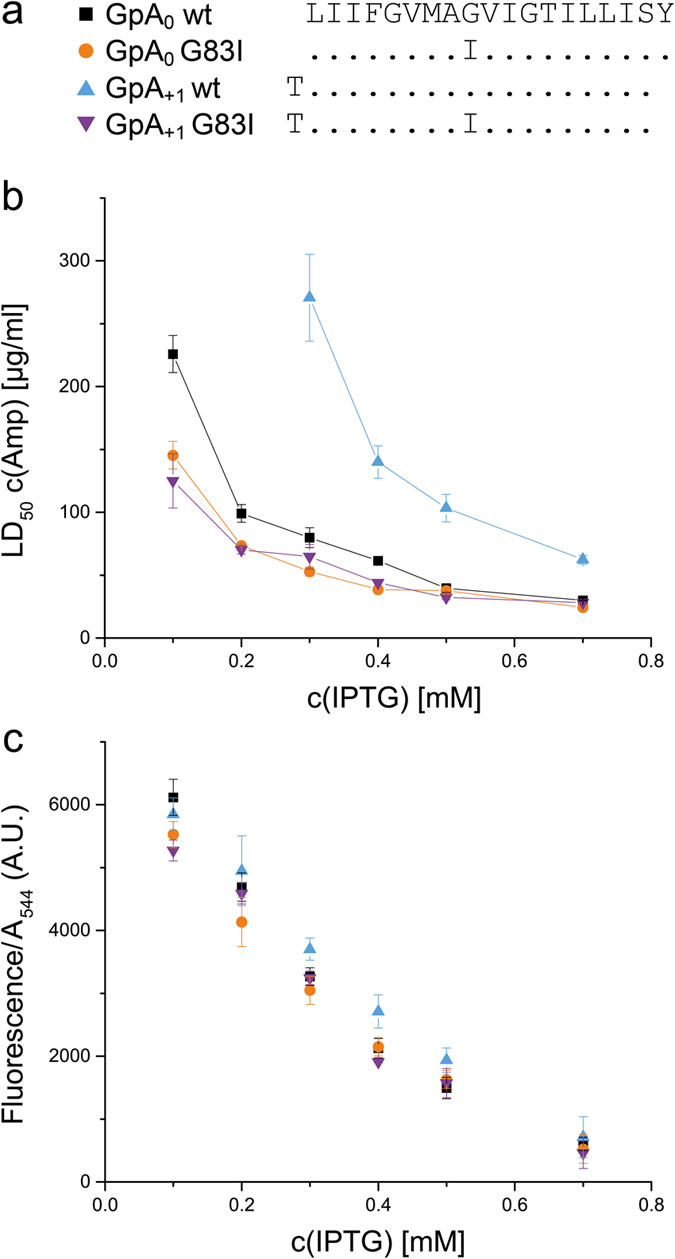
(a) GpA wild-type and mutant TMD frames tested. (b) Effect of IPTG concentration on ampicillin resistance. Lowering the activity of the pBAD promoter by increasing the IPTG concentration45 (133 μM arabinose) influences LD50 in a way that depends on TMD orientation. No data points are given for GpA+1 wt at 0.1 mM and 0.2 mM IPTG since the corresponding LD50 values were too high for reliable determination. (c) For control, protein expression was analyzed by GFP fluorescence that was normalized to cell density (A544, A.U. = arbitrary units). Even if the GFP moiety is proteolytically cleaved off from part of the BLa proteins during expression (see: Supplementary Fig. S4d), GFP fluorescence represents the amount of originally expressed protein. Note that the expression level varies as a function of induction but not of TMD orientation or sequence. All TMDs are expressed in BLaTM 1.2 in E. coli JM83 where the expression level is too low for detection by Western blotting. Means ± SEM, n = 3.
