Figure 4. TGFβ signaling modulates Gli2 and PTHrP expression.
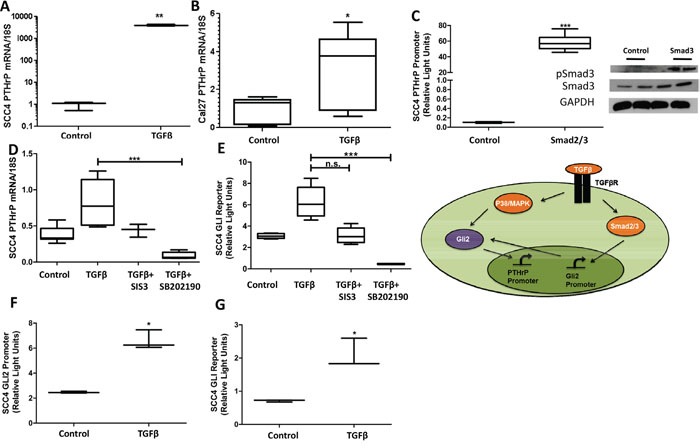
A&B. TGFβ signaling increased PTHrP expression.qRT-PCR was used to determine PTHrP mRNA levels of SCC4 and CAL27 cells that were treated with TGFβ or the buffer control. TGFβ treatment significantly increased PTHrP in all cell lines tested. C. Smad2/3 over-expression increased PTHrP expression. SCC4 cells were co-transfected to overexpress equal amounts of Smad2 and Smad3 (see insert for protein confirmation by Western blot), as well as a PTHrP firefly luciferase reporter plasmid and a constitutively active Renilla luciferase reporter plasmid. 48 hours after transfections, cells were harvested and firefly activity quantified. Smad over-expression significantly increased PTHrP promoter expression. D&E. Canonical and non-canonical TGFβ inhibition decreased Gli activity and PTHrP expression. qRT-PCR was used to determine PTHrP mRNA levels of SCC4 cells treated with TGFβ, and SIS3, a Smad3 inhibitor, or SB202190, a p38/MAPK inhibitor. While Smad3 inhibition trended to significantly decrease Gli activity and PTHrP expression, only p38/MAPK inhibition significantly decreased both. F&G. TGFβ signaling increased Gli2 promotor and protein activity. SCC4 cells were co-transfected with an endogenous Gli2 promoter construct, or a Gli2 protein reporter construct, as well as a constitutively active Renilla luciferase reporter plasmid. 24 hours after transfections, cells were treated with TGFβ or the buffer control and harvested 24 hours later before firefly activity was quantified. Both promoter and protein activity of Gli2 was significantly increased with TGFβ signaling. Inset demonstrates the dual role TGFβ signaling has on increasing Gli2 at the level of mRNA as well as protein.
