Figure 2. NOD/SCID-γ (NSG) mouse in vivo studies.
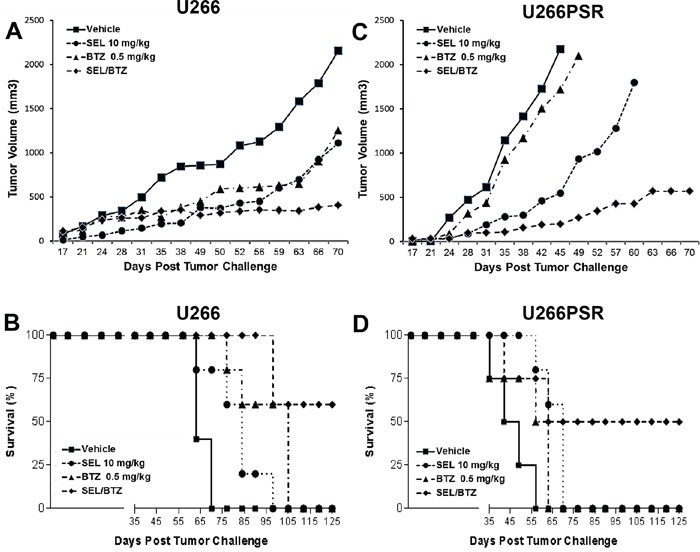
NSG mice (n=5 per group) were challenged subcutaneously with 107 U266 (A/B) or 106 proteasome inhibitor (PI)-resistant U226PSR (C/D) human MM cells. Mice were treated twice weekly (Monday, Thursday) with selinexor +/− BTZ. selinexor was administered by oral gavage and BTZ by intraperitoneal injection. A/C. Tumor growth with selinexor and BTZ. BTZ/selinexor combination reduced tumor growth compared with single-agent BTZ (P = 0.022) or vehicle control (P = 0.0014). B/D. Survival with selinexor and BTZ. In NSG mice challenged with U266 tumors, selinexor/BTZ treatment improved survival compared with vehicle (P = 0.0006) or single-agent selinexor (P = 0.0010) or BTZ (P = 0.0072). Treatment of PI-resistant PSR tumors with selinexor/BTZ also improved survival compared with vehicle control (P = 0.0001) and single-agent BTZ (P = 0.0001) or selinexor (P = 0.0085). Toxicity, assessed by weight loss (<10%), was minimal in all treatment groups.
