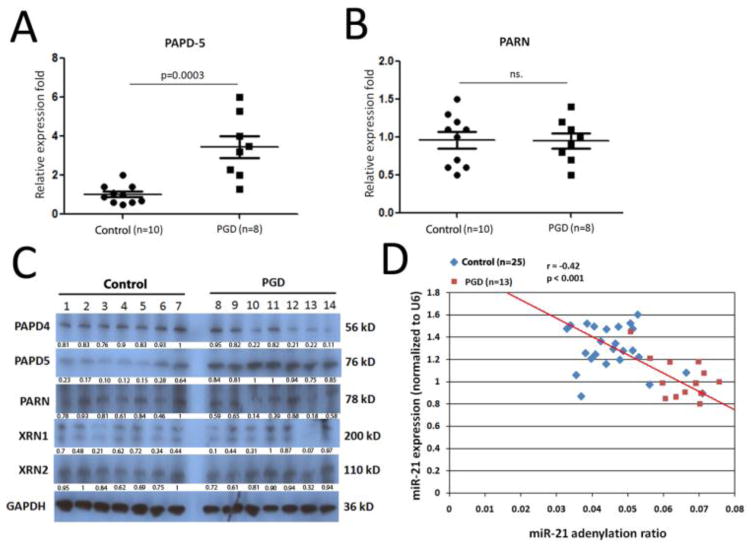
Figure 7.
Enhancement of the miR-21 degradation pathway activation in lungs with primary graft dysfunction (PGD). (A and B) Quantitative expression of PAPD-5 and PARN mRNAs was assessed by qRT-PCR on RNA samples of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells from 10 control lungs and 8 lungs with severe PGD. Comparisons were performed with the Mann Whitney U-test. (C). Western blot assay on PAPD-4, PAPD-5, PARN, XRN-1, and XRN-2 protein levels in BAL cell lysates from 7 control and 7 donor lungs with severe PGD. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as loading control. Protein quantification was performed by bandscan and densitometry analysis with optical density for PAPD-4, PAPD-5, PARN, XRN-1, and XRN-2. (D). miR-ID® miRNA quantification assays was used to specifically detect the relative expression level of the miR-21+CA and miR-21+C isomiRs. Donor BAL samples from 25 control and 13 PGD were included here. The P-values were calculated using Pearson’s correlation tests.