Figure 6.
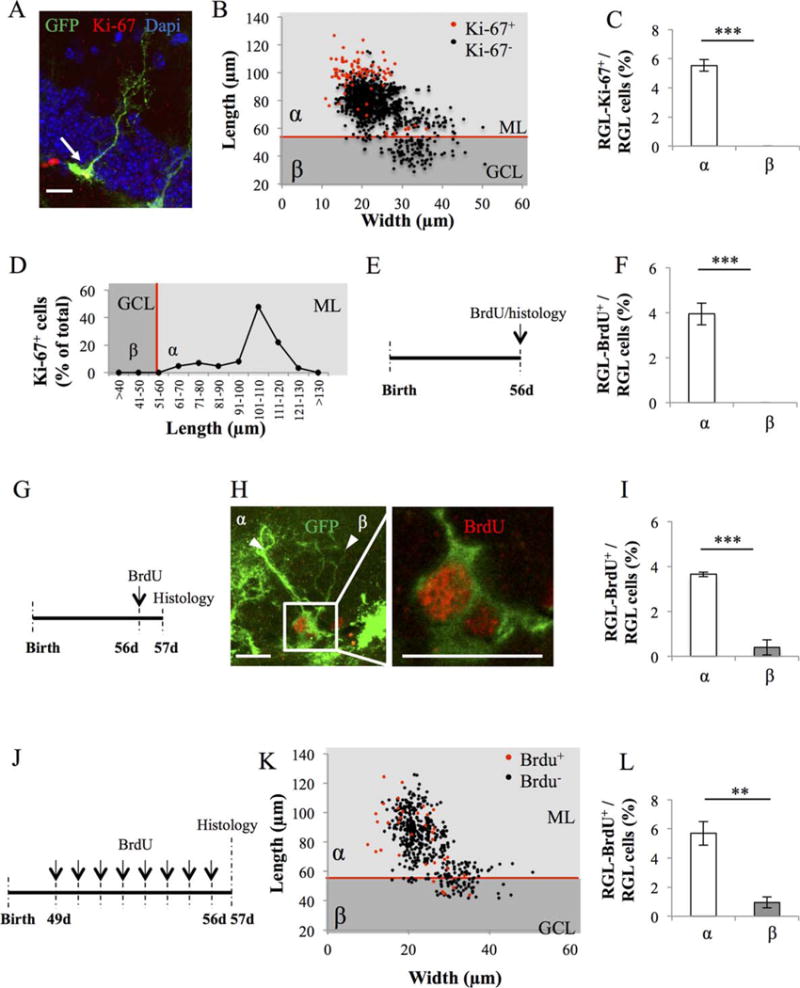
Proliferative properties of types α and β cells in GFAP-GFP mice. (A): Confocal maximal projection micrograph of radial glia-like (RGL) cell (green), immunostained for Ki-67 (red). (B): Scatter graph of RGL cell dimensions. Red dots: Ki-67+ cells N = 86, black dots Ki-67− cells N = 1469. (C): Histogram showing the percentage of types α and β cells expressing Ki-67. Bilateral Student’s t test. (D): Line graph representing the proportion of RGL cells expressing Ki-67 according to their length. (E): Experimental timeline: mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) at doses of 100 mg/kg in saline, three times at 2-hour intervals and killed 2 hours after the last injection. (F): Histogram showing the percentage of types α and β cells expressing bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU). N = 500 cells. Bilateral Student’s t test. (G): Experimental timeline: mice were injected i.p. at doses of 100 mg/kg in saline, three times at 2-hour intervals and killed 24 hours after the last injection. (H): Confocal maximal projection micrograph of types α and β cells expressing BrdU. Confocal micrograph of one focal plan showing the immunoreactive cells Scale bar: 20 μm (I) Histogram showing the percentage of types α and β cells expressing BrdU. N = 500 cells. Bilateral Student’s t test. (J): Experimental timeline: Mice were injected daily with BrdU for 8 consecutive days, starting at 49 days after birth. One day after the last injection, they were killed and prepared for histology. (K): Scatter graphs representing the dimensions of RGL cells after immunostaining for BrdU (red dots: BrdU+ cells N = 35, black dots BrdU− cells N = 492) (L): Histogram showing the proportion of types α and β cells that incorporated BrdU. Bilateral Student’s t test. Scale bar: 20 μm. Each value represents the mean ± SEM. **, p < 0.01 ***, p < 0.001. Abbreviations: BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; GCL, granule cell layer; GFP, green fluorescent protein; ML, molecular layer; RGL, radial glia-like.
