Figure 3.
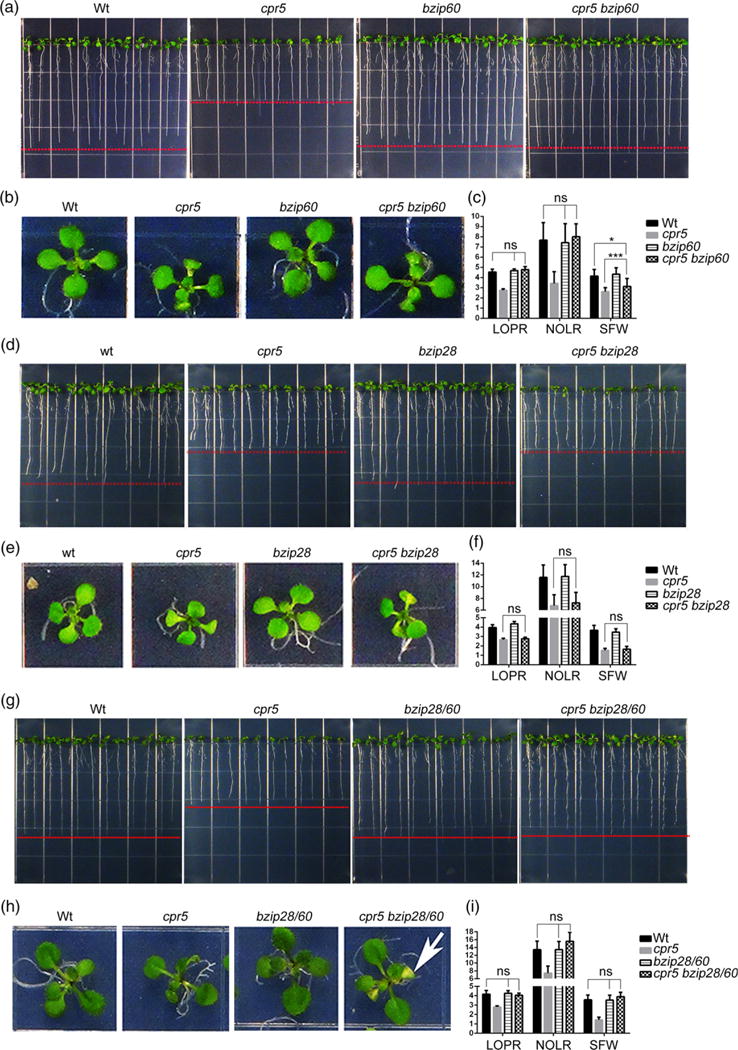
The role of CPR5 in primary root growth is affected by bZIP60, while it is independent from bZIP28.
(a), (b), (d), (e), (g), (h) Seedlings were germinated on 1/2 Linsmaier and Skoog medium for 12 days vertically (a, d, g) and horizontally (b, e, h). (c), (f), (i) Absolute growth values of single and high-order mutants of cpr5, bzip28 and bzip60 as indicated in (a, d, g). LOPR, length of primary root; NOLR, number of lateral roots; SFW, shoot fresh weight; Wt, wild type. Error bars represent SD; n = 24 for each genotype. The P-values were obtained using Student’s t-test for each comparison. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. The arrow in (h) indicates the occurrence of necrosis in the cotyledons that is typical of cpr5.
