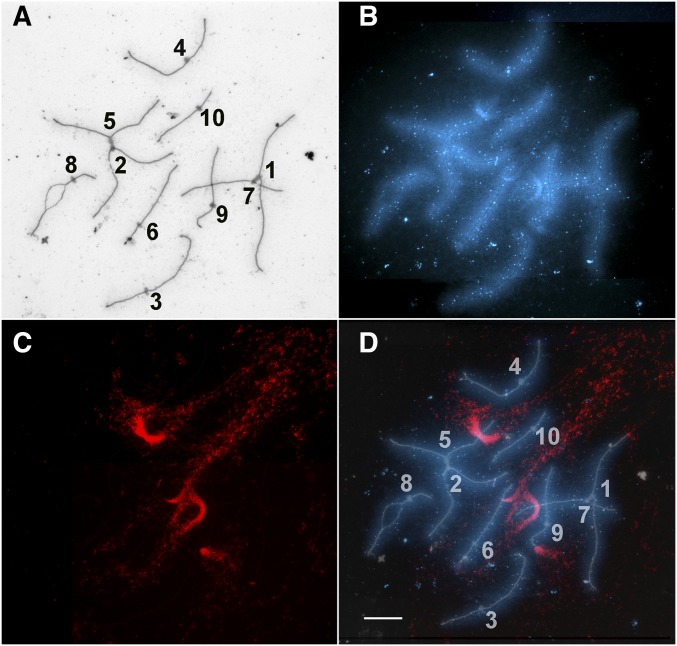
Figure 4.
Maize pachytene SC spread. (A) SCs and kinetochores stained with silver. Each SC has been identified on the basis of relative length and arm ratio, and numbered at its kinetochore. Kinetochores on SCs 1 and 7 are stuck together as are the kinetochores on SCs 2 and 5. SC 8 is partially asynapsed. (B) The same SC spread visualized with DAPI fluorescence. Due to the hypotonic spreading procedure, the chromatin loops around the SCs are dispersed laterally as a fuzzy blue coat along the length of each SC. (C) The FISH signal (red) of the 180-bp repeat for this SC spread. (D) Merged images of silver-stained SCs (inverted to appear white), DAPI-stained chromatin (blue), and the 180-bp knob repeat (red). The chromatin of the interstitial knobs (on the long arms of SCs 5, 6, and 7) occupies well-defined SC segments, and at least some chromatin loops from the knobs (red) extend much farther from their SC attachment sites than chromatin loops in distal euchromatin and pericentric heterochromatin. For the terminal knobs (on the short arms of SCs 1 and 9) the loops also extend far from their attachment sites, but the loops appear to extend from the tips of the SCs without defining distinct terminal SC segments. Bar, 5 µm. SC, synaptonemal complex.