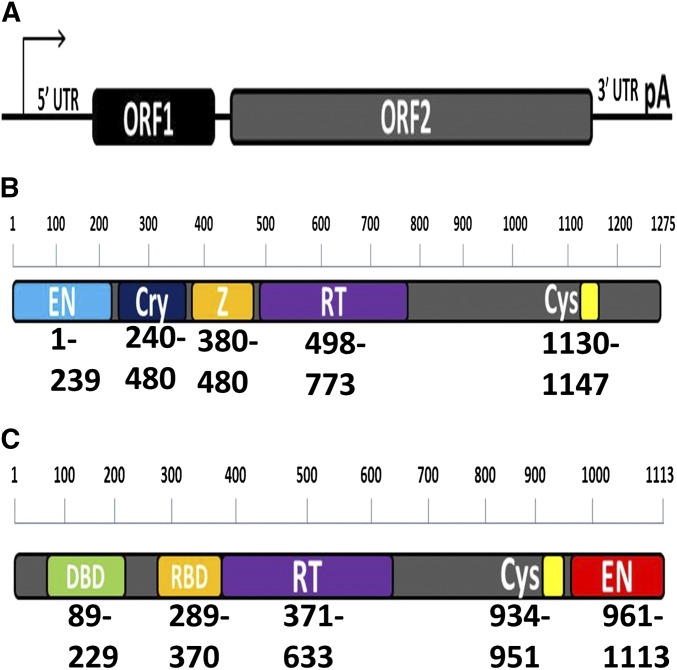
Figure 1.
Reported functional domains/regions in the L1 ORF2p and R2 ORFp. (A) Schematic representation of L1. L1 is comprised of a 5′ UTR containing internal Pol II promoter, ORF1, ORF2, a 3′ UTR, and a Poly(A) signal. ORF1 codes for the structural ORF1p, while ORF2 codes for the enzymatically active ORF2p. (B) Human ORF2p schematic. The human ORF2p has five functional regions, two of which are known to have enzymatic activity. The enzymatically active domains of the ORF2p are the EN domain (light blue) and RT domain (purple). The ORF2p also contains a Cysteine-rich domain (Cys, yellow) and Z domain (Z, orange). The Z domain contains a PCNA binding domain necessary for both L1 and Alu retrotransposition. The recently described Cryptic region (Cry, dark blue) contains amino acids important for retrotransposition. Amino acid boundaries of the domains are indicated below. Amino acid scale bar is displayed above the schematic. (C) Schematic of annotated functional domains/regions within the R2 ORFp. The R2 ORFp contains five annotated regions. These include two enzymatically active domains: an RT domain (purple) and an EN domain (red). The R2 ORFp also contains a DNA binding domain (DBD, green) and an RNA binding domain (RBD, orange), which has sequence homology to the ORF2p Z domain. The R2 ORFp also has a Cystein-rich motif (Cys, yellow), similar to the Cys domain of the L1 ORF2p.