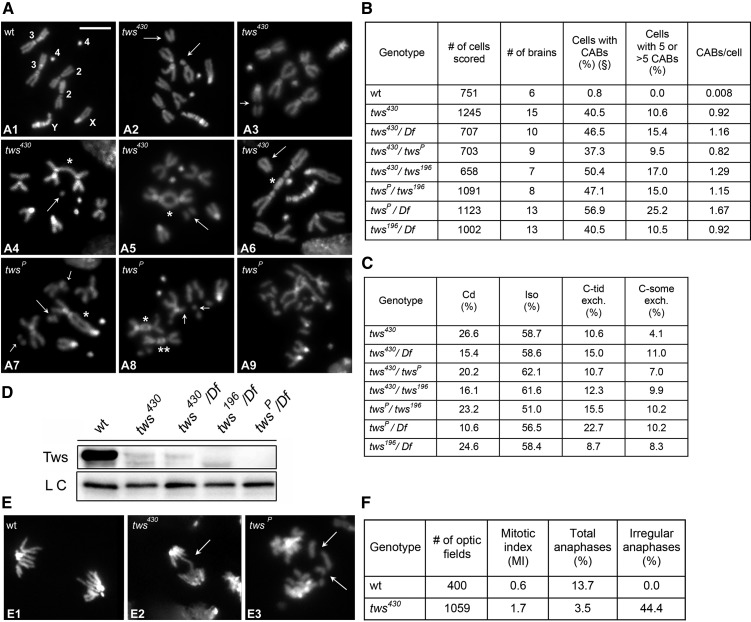
Figure 1.
tws mutants exhibit frequent CABs. (A) Examples of CABs: (A1) Wild-type male metaphase. (A2) Isochromatid deletion (iso) of a major autosome (Au), arrows. (A3) Iso of the X chromosome, arrow. (A4) Asymmetric Au-Au chromatid exchange (*) with acentric fragment (AF; arrow). (A5) Au-Au dicentric chromosome (*) with the AF (arrow). (A6) Au-Au dicentric chromosome (*) with the AF (arrow). (A7) Au-XL dicentric chromosome (*) with AF (big arrow) and autosomal isochromatid deletion (small arrows). (A8) XR-Au (*) and Au-Au (**) dicentric chromosomes with the AFs; and chromatid deletion (Cd) of a major autosome (arrows). (A9) Metaphase with extensive chromosome fragmentation. Bar, 5 μm. (B) Frequencies and (C) types of CABs observed in tws mutants. (D) Western blotting showing strong reductions of the Tws protein in different tws mutants. (E) Examples of irregular anaphases: (E1) wild type, (E2) mutant anaphase with a chromatin bridge, (E3) mutant anaphase with lagging acentric fragments. (F) Mitotic parameters in wild-type and tws mutant brains. The MI is the average number of mitotic figures per optic field (see Materials and Methods). #, number; C-tid exch., chromatid exchange; C-some exch., chromosome exchange; LC, loading control; wt, wild type.