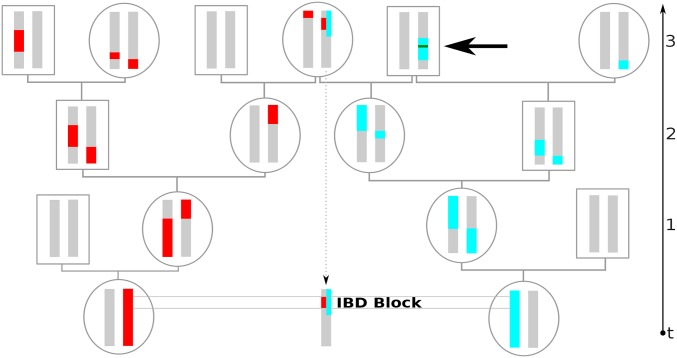
Figure 1.
Example of an IBD block co-inherited from a common ancestor three generations back. Going back in time, recombination splits up genetic ancestry (colored red and blue here) into blocks distributed among ancestors. If, as depicted here, such ancestral blocks overlap in a recent common ancestor, the intersecting stretch of the genome will be shared and both individuals will carry few distinguishing mutations. Here, we define IBD blocks to be delimited by any recombination events on the genealogical path to the most recent common ancestor. Thus, the recombination events that are fused again quickly by inbreeding loops, as depicted by the blue chromosome (thick arrow), also delimit IBD blocks. However, this recombination is not detectable in practice, and the two adjacent IBD blocks would be identified as one long IBD segment.