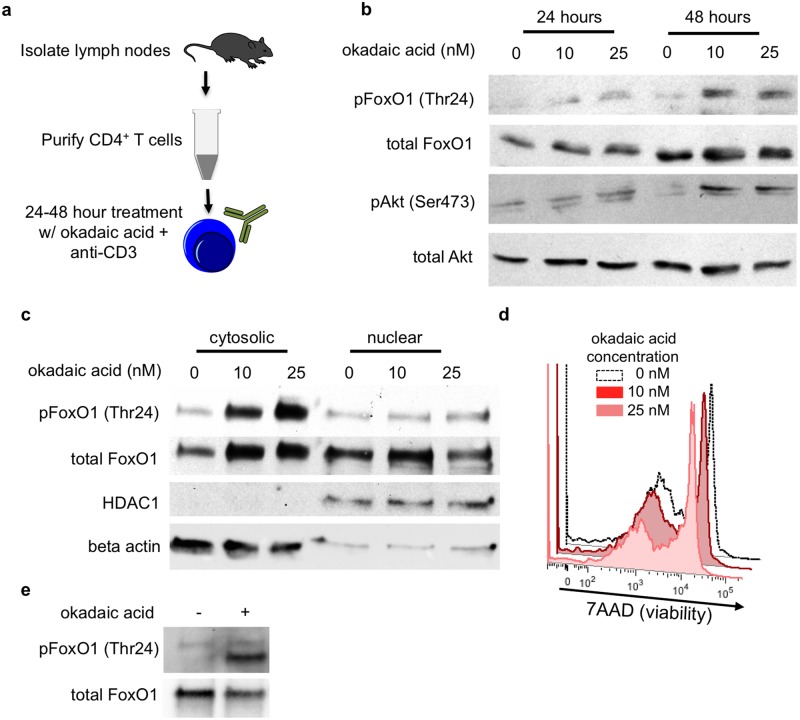
Fig 2. PP2A inhibition increases FoxO1 phosphorylation and cytosolic localization in CD4+ T cells.
(a) Primary CD4+ T cells were negatively selected from the lymph nodes of 6–8 week old mice by magnetic cell sorting. CD4+ T cells were treated with the indicated dosages of okadaic acid for up to 48 hours in cultures supplemented with 1μg/mL anti-CD3. (b) Western blot analysis of FoxO1 phosphorylation at Thr24 and Akt at Ser 473. (c) Western blot analysis of FoxO1 localization in fractionated CD4 cells. Beta-actin and HDAC were used as cytoplasmic and nuclear controls respectively. (d) Viability of CD4+ T cells in culture after 48 hours with the indicated concentrations of okadaic acid. (e) Western blot analysis of in vitro phosphatase assay. Immunoprecipitated FoxO1 was treated with PP2A +/- 100nM okadaic acid. b, c and d are representative data from 3 individual experiments; e is representative of 2 experiments.