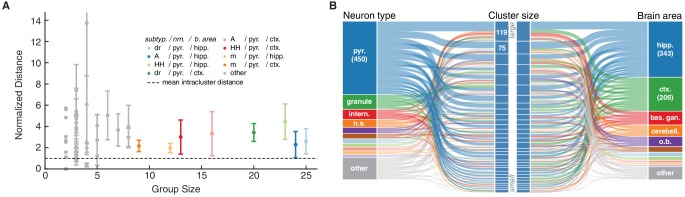
Figure 5. Ion channel model groups defined by common subtype, neuron type and brain area show variability in behavior.
(A) Kv models are grouped by common subtype, neuron type, and brain area. The mean pairwise distance in score space between all models within a group is plotted against group size, with errorbars corresponding to the first and third quartiles (middle 50% of distances). The largest eight groups are shown in color. Distances are normalized relative to the mean pairwise distance between models in the same cluster (dashed line; averaged across all clusters with at least one pairwise distance greater than zero, 43 of 60 clusters). Most groups have a larger mean distance than the average cluster (above the dashed line). (B) ‘Sankey’ relational diagram for metadata, neuron type, cluster identification and brain area, for the Kv ion type class. Bars are stacked histograms, that is, the height of the bars indicates the relative number of models. Left column: partition of channels by 11 most prevalent neuron types. Middle column: partition of channels into assigned clusters. Right column: partition of channels by 11 most prevalent brain areas. Links between columns are colored according to neuron type (left) and brain area (right). Numbers in the left/right column are the number of channels per label. pyr: pyramidal, intern.: interneuron, n.s.: not specified, hipp.: hippocampus, ctx: cortex, bas. gan.: basal ganglia, cerebell: cerebellum, o.b.: olfactory bulb.