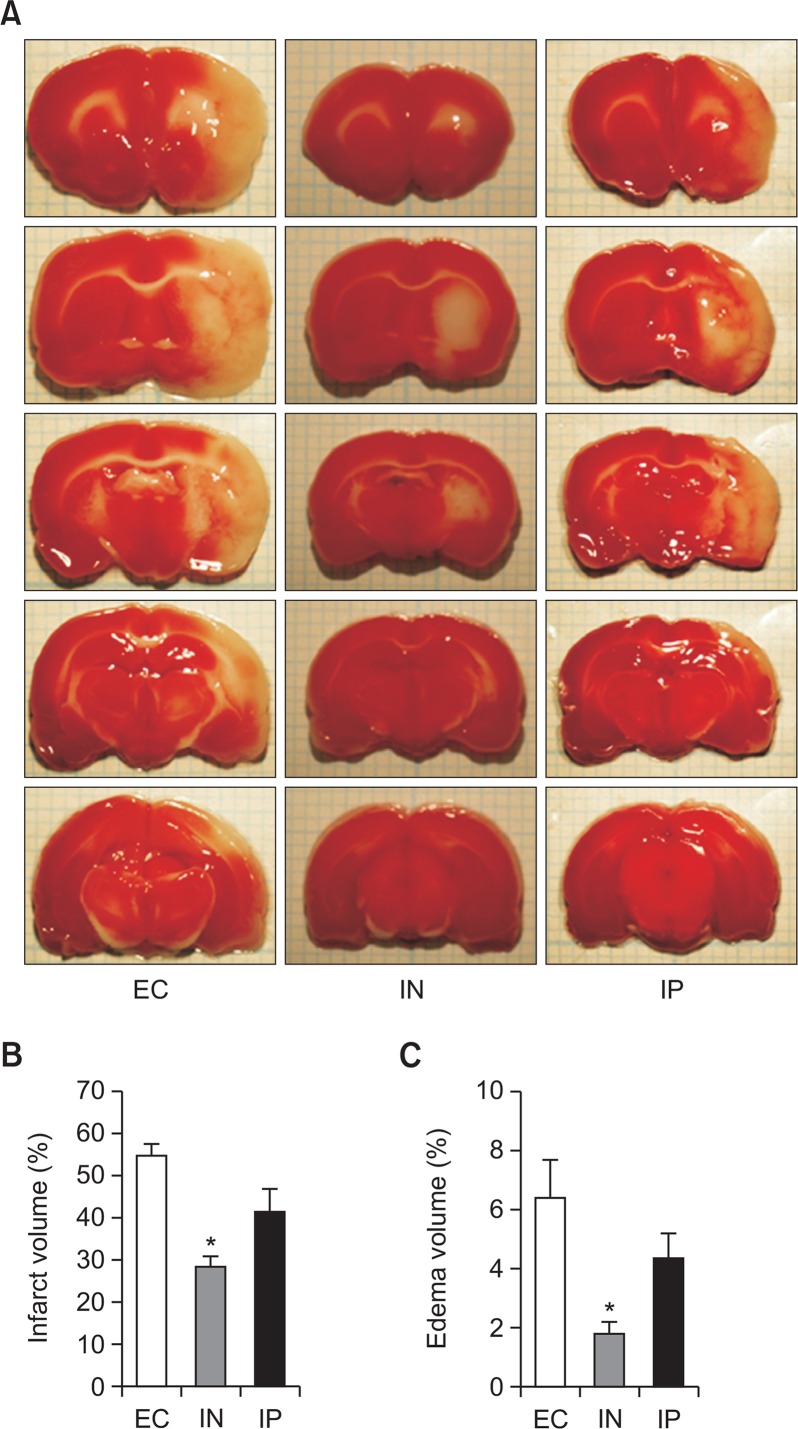
Fig. 1.
Neuroprotective effects of intranasal IL-1RA against transient cerebral ischemia. Brain damage is assessed by using TTC staining 7 days after the ischemic insult (cerebral ischemia for 1 h). The EC, IN, and IP groups received vehicle, intranasal IL-RA, and intraperitoneal IL-1RA, respectively. Representative TTC staining images of brain sections for each group (A). Quantitative comparisons of infarct volume (B) and edema volume (C) (n=5 in the EC group, n=7 in the IN group, and n=6 in the IP group). Values are shown as mean (SEM). *p<0.005, versus the EC group by oneway analysis of variance with Bonferroni post hoc test.