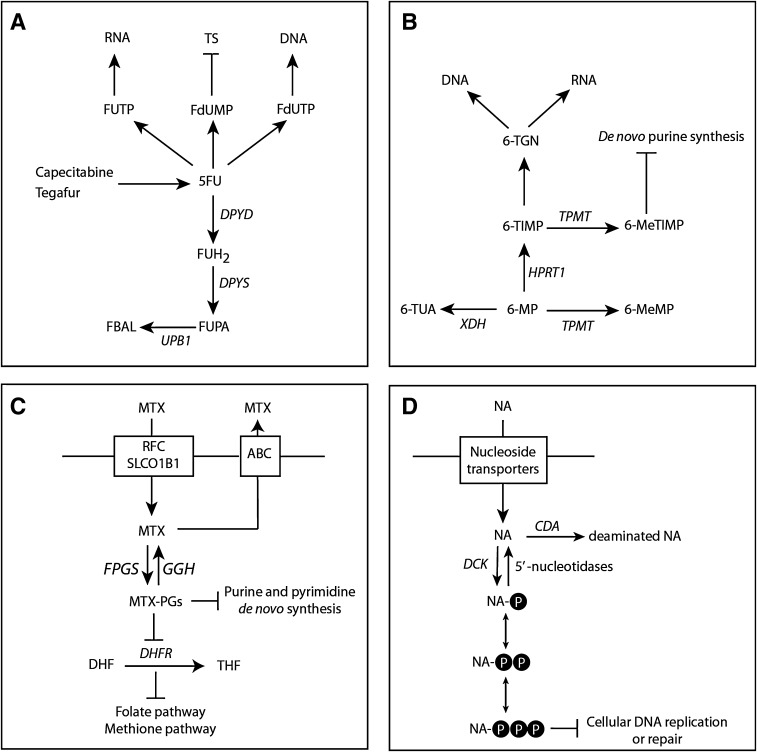
Fig. 1.
Metabolism of drugs interfering with purine and pyrimidine synthesis. a Metabolism of fluoropyrimidine-containing drugs. b Thiopurine metabolism. c Methotrexate metabolism. d Nucleoside metabolism. ABC adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette family of transporters, CDA cytidine deaminase, DCK deoxycytidine kinase, DHF dihydrofolate, DHFR dihydrofolate reductase, DPYD dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, DPYS dihydropyrimidinase, FBAL fluoro-β-alanine, FGPS folylpolyglutamate synthase, FUH 2 5-fluoro-dihydrouracil, FUPA fluoro-β-ureidopropionate, GGH γ-glutamyl hydrolase, HPRT1 hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase, MTX methotrexate, MTX-PGs MTX-polyglutamate, NA (deoxy)nucleoside analogs, RFC reduced folate carrier, SLCO1B1 solute carrier organic anion transporter B, THF tetrahydrofolate, dehydrogenase/oxidase, TPMT thiopurine-S-methyltransferase, UPB1 β-ureidopropionase, XDH xanthine, 5-FU 5-fluorouracil, 6-MeMP 6-methylmercaptopurine, 6-MeTIMP 6-methylthioinosine monophosphate, 6-MP 6-mercaptopurine, 6-TGN 6-thioguanine nucleotides, 6-TIMP 6-thioinosine monophosphate, 6-TUA 6-thiouric acid