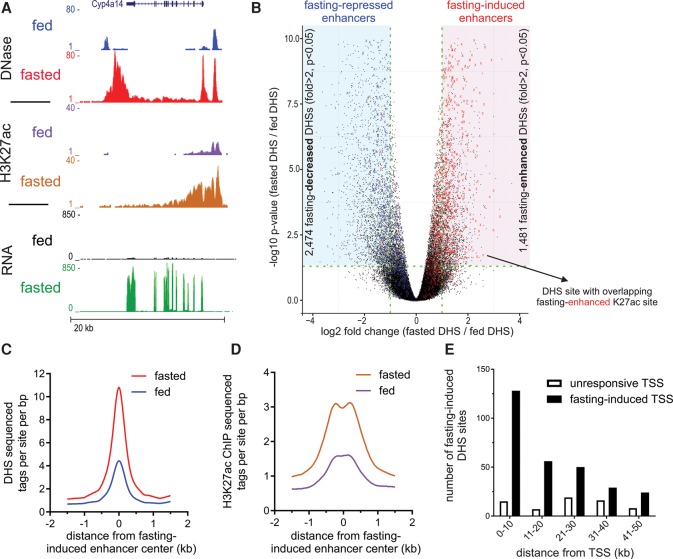
Figure 1.
Fasting substantially affects the hepatic chromatin landscape, exposing “fasting-induced enhancers.” (A) Genome browser tracks of the Cyp4a14 locus depicting increases in DNase I hypersensitivity, H3K27 acetylation, and RNA levels upon fasting (24 h; three animals were assayed in each group). (B) Volcano plot of all hepatic DNase I hypersensitive sites. DHS sites within the shaded areas show a significant change in accessibility upon fasting (twofold or greater, adjusted P-value ≤0.05). DHS sites overlapping with fasting-induced H3K27ac sites are depicted by a red X. These DHS sites tend themselves to be enhanced by fasting (mostly to the right). DHS sites overlapping with fasting-repressed H3K27ac sites are depicted by a blue X. These DHS sites tend themselves to be decreased by fasting (mostly to the left). (C,D) DHS (C) and H3K27ac (D) ChIP-seq tag density at fasting-induced enhancers in the fed and fasted states. (E) The number of DHS sites in the vicinity of fasting-induced genes (n = 1055) or unresponsive genes (random set, n = 1055) was plotted as a function of distance from gene transcriptional start site (TSS; plotted in 10-kb bins).