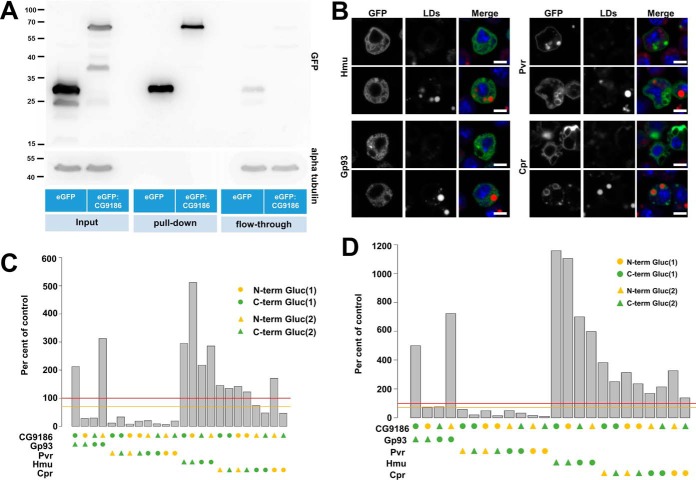
Fig. 4.
Identification and confirmation of CG9186 interaction partners by mass spectrometry and the luciferase complementation PPI assay. A, Extracts of Drosophila Kc167 cells stably expressing either GFP alone or GFP fused to CG9186 were subjected to immunoprecipitation using GFP-specific antibodies. Western blot analysis of SDS-PAGE separated samples using a GFP specific antiserum demonstrated efficient purification of GFP alone and GFP-tagged CG9186 (compare enrichment between pull-down and flow-through). Probing the membrane with an alpha tubulin-specific serum (shown below) demonstrates absence of tubulin in the pull-down fractions and comparable amounts in the input and flow-through fractions. B, Localization of candidate CG9186 interactors (supplemental Fig. S2) in Drosophila Kc167 tissue culture cells. GFP fusions of Hemomucin (Hmu), Cytochrome P450 reductase (Cpr), PDGF- and VEGF-receptor related (Pvr) or the Glycoprotein 93 (Gp93) were expressed in the presence (top rows) or absence of OA (bottom rows). In the absence of OA Hmu, Cpr, and Gp93 localize in a reticular pattern. Pvr is enriched at the plasma membrane, as reported previously (72, 73), and on intracellular membranes. The localization of Gp93 and Pvr does not change with OA addition, whereas Cpr and Hmu are now found in the vicinity of LDs. (C, D) In the split luciferase complementation assay tested against CG9186, Pvr did not show complementation of the luciferase activity, whereas Hmu, Cpr or Gp93, displayed significant luciferase activity, both in the absence (C) and presence (D) of LDs. Threshold levels are indicated as in Fig. 3. Scale bars represent 5 μm.