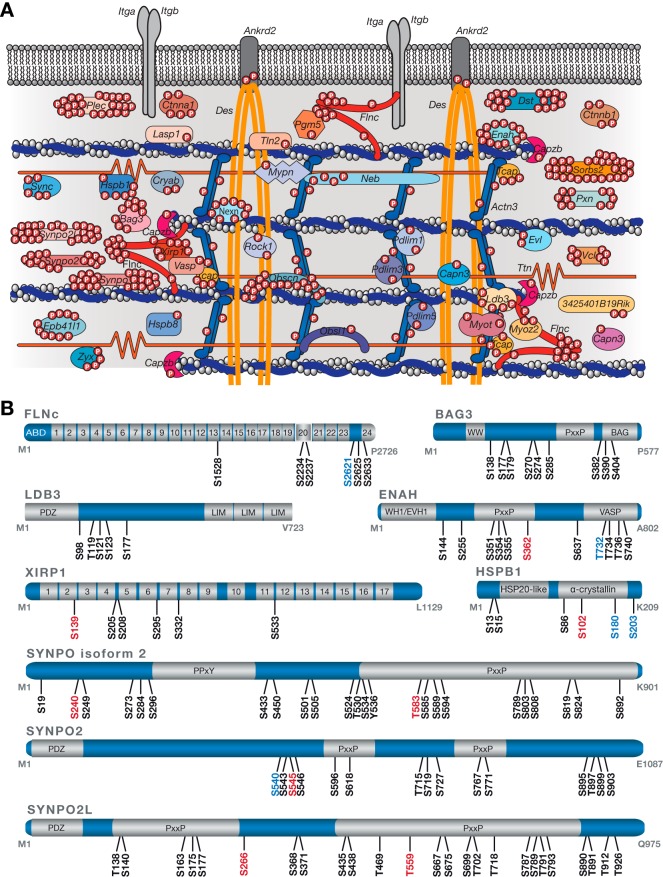
Fig. 3.
A site-specific protein phosphorylation map of the myofibrillar Z-disc proteome from mouse skeletal muscle cells. A, Schematic overview of the Z-disc phosphoproteome. 44 genes (encoding for 51 proteins) were found to be modified by a single or multiple phosphate groups accounting for 70% of the known Z-disc proteome. Phosphosites localized in the Z-disc-associated regions of the two structural proteins titin (12 p-sites) and desmin (14 p-sites) are not depicted. B, Schematic illustration of highly phosphorylated Z-disc proteins. Localized phosphosites (mouse) are color-coded based on information provided by the PhosphoSitePlus database (version 07.01.2016) with black for known sites, blue for phosphosites known by similarity to orthologues sites in human proteins, and red for newly identified sites. Information about protein domains was retrieved from the UniProt and InterPro database. Immunoglobulin-like domains in FLNc and XIRP1 are numbered. ABD, actin-binding domain; BAG, Bcl2-associated athanogene; PDZ, post synaptic density protein, Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor, and zonula occludens-1 protein; PxxP, proline-rich; PPxY, proline-proline-x-tyrosine; VASP, vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein; WH1, WASP-homology/EVH1, Ena/VASP homology 1.