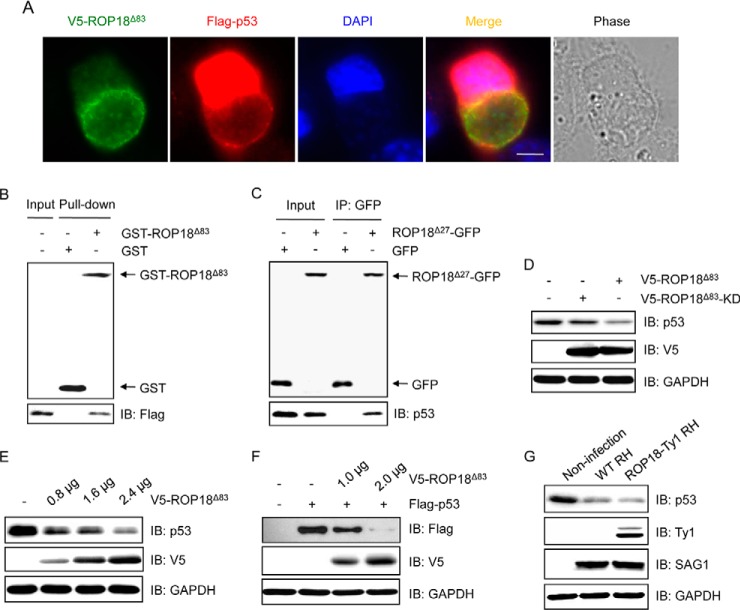
Fig. 4.
ROP18 interacts with p53 and promotes its degradation. A, HeLa cells were transfected with V5-ROP18Δ83 and FLAG-p53 followed by infection with tachyzoites of RH strain for 24 h, and then immunofluorescence staining was performed with mouse monoclonal anti-V5 (green) and rabbit polyclonal anti-FLAG (red) antibodies. DAPI (blue) was used to visualize cell nuclei. Phase, bright field; bar, 5 μm. B, GST pulldown assay was performed using GST-ROP18Δ83 protein purified from yeast and lysates of 293T cells overexpressing FLAG-p53. IB, immunoblot. C, 293T cells were transfected with ROP18Δ27-GFP expression plasmid, and coimmunoprecipitation was performed with anti-GFP, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. D, 293T cells were transfected with V5-ROP18Δ83 or V5-ROP18Δ83-KD plasmids for 36 h, and the total cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. E, lysates of 293T cells transiently transfected with the indicated amounts of V5-ROP18Δ83 plasmids were detected by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. F, 293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated amounts of V5-ROP18Δ83 and 1 μg of FLAG-p53 plasmids. 36 h after transfection, total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. G, lysates of 293T cells infected with wild-type (WT) RH and ROP18-Ty1 RH strains were detected by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. SAG1 and GAPDH were used as loading controls.