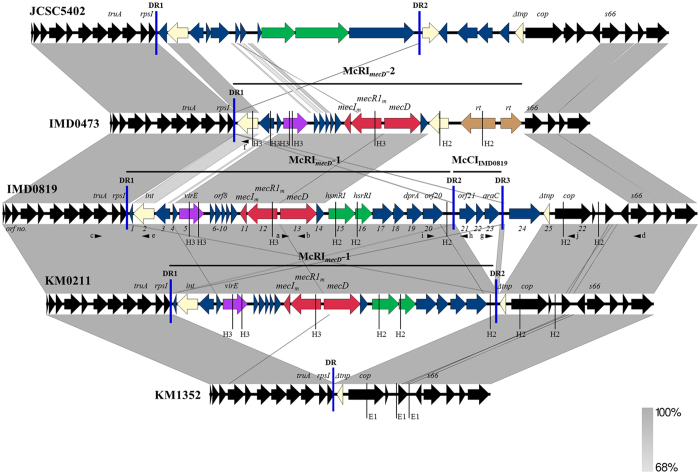
Figure 3. Structures of McRImecD-1 and McRImecD-2 and flanking sequences.
Comparison was performed with sequences of M. caseolyticus strains JCSC5402 (Genbank acc. no. NC_011999, position 215180–250630), IMD0473 (Genbank acc. no KY013610), IMD0819 (Genbank acc. no KY013611), KM0211 (Genbank acc. no KY013612) and KM1352 (Genbank acc. no KY013613) using Easyfig software57. Gray areas indicate regions with between 68% to 100% nucleotide sequence identity. Regions encompassing McRImecD-1, McRImecD-2 and McCIIMD0819 are indicated by horizontal black lines and flanking direct repeats (DRs) by vertical blue lines. The open reading frames (orfs) are represented by arrows: mecD, mecR1m and mecIm are shown in red, orfs encoding integrase (int) or transposase (tnp) are shown in yellow, reverse transciptases (rt) in beige, orfs associated with restriction-modification in green and virulence-associated orfs in mauve; the orfs occurring in all M. caseolyticus strains are shown in black and additional strain-specific orfs in blue. The primers used in this study are indicated by small black arrowheads (a), mecD-F; (b), mecD-R; (c), truA-F; (d), s66-R; (e), int-0819-F; (f), int-0473-F; (g), araC-F; (h), orf21-R; (i), orf20-F; (j), cop-R) and cleavage sites for restriction endonucleases HindIII (H3) and HincII (H2) and EcoRI (E1) by thin vertical lines.