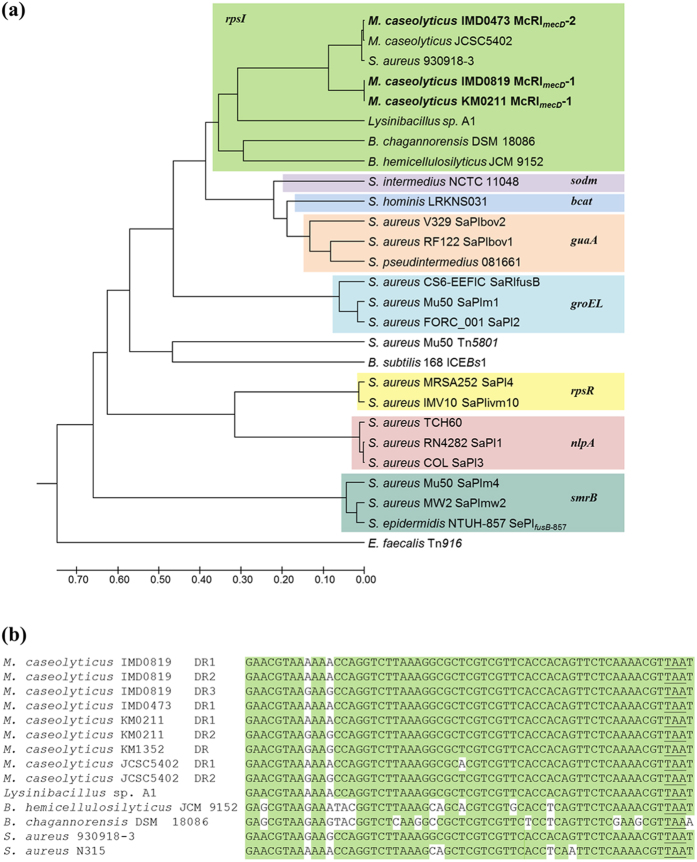
Figure 4.
(a) Phylogenetic tree of integrases of the tyrosine recombinase family. Colored boxes group members that share homologous integration sites (rpsI, gene for 30S ribosomal protein S9; sodm, superoxide dismutase gene; bcat, gene for branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase; guaA, GMP synthetase gene; groEL, chaperonin gene; rpsR, gene for 30S ribosomal protein S18; nlpA, gene for component of ABC-type metal ion transport system; smrB, gene for SsrA-binding protein). Analysis was performed for amino acid (aa) sequences using the UPGMA method in MEGA756. Host strains and genetic elements if known are indicated. References for the used sequences can be found in Supplementary Table S3. (b) Putative core attachment sites recognized by rpsI-associated integrases. For M. caseolyticus strains, the imperfect direct repeats (DR) carrying the att consensus sequence are indicated. For all other species the att site found at the 3′ end of the rpsI gene is given. The rpsI stop codon is underlined. Positions that hold variant bases are unshaded. All species, except S. aureus N315 and M. caseolyticus KM1352, carry an integrase gene downstream of rpsI.