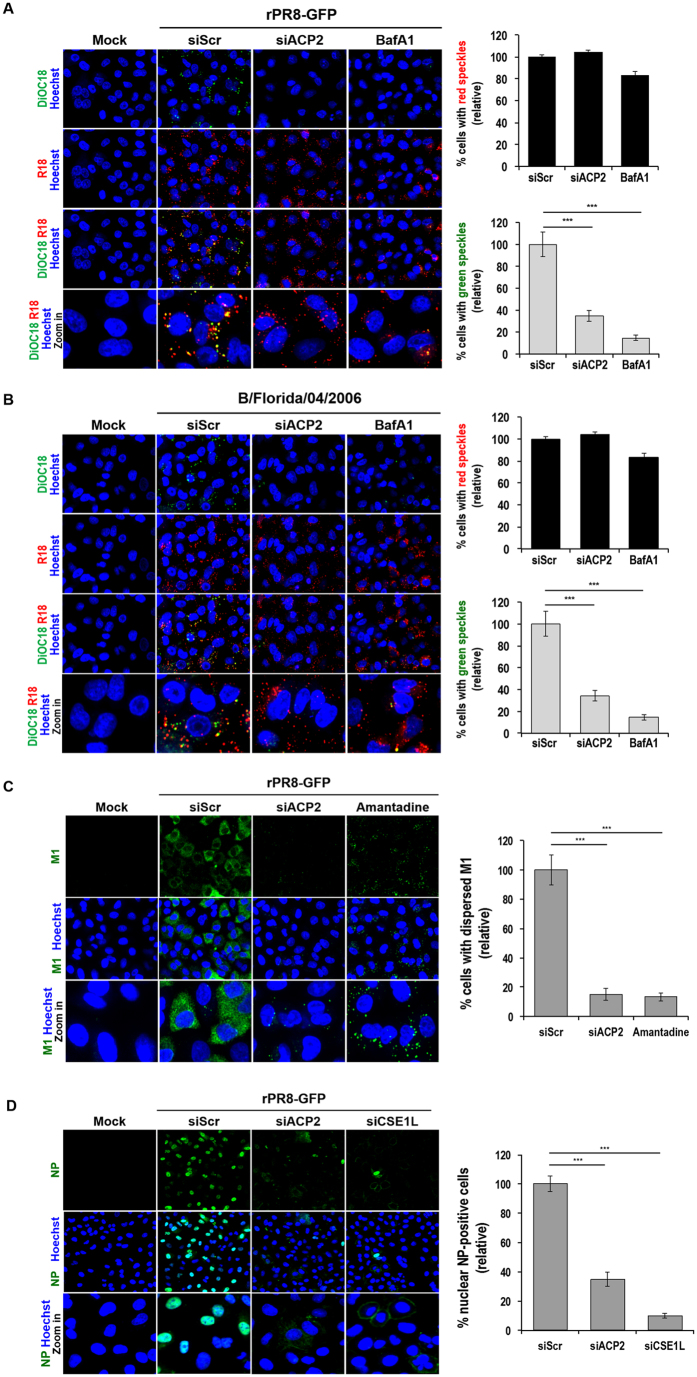
Figure 5. ACP2 is crucial for membrane fusion during entry of influenza A and B viruses.
(A and B) ACP2 knockdown impaired the fusion step between viral and endosomal membranes. A549 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs at 37 °C for 48 hours prior to infection with viruses rPR8-GFP (A) or B/Florida/04/2006 (B) that had been labeled with R18 and DiOC18 at an MOI of 100 at 4 °C for 1 hour. Cells were then washed with PBS and incubated at 37 °C for an additional 1.5 hours with or without 0.1 μM of bafilomycin A1 (BafA1) prior to fixation. The number of the cells with red (R18) or green (DiOC18) speckles was quantified using in-house-developed image-mining (IM) software and normalized to siScr control cells (right panel). (C) Cytoplasmic M1 expression was decreased in ACP2-depleted cells. A549 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs at 37 °C for 48 hours prior to rPR8-GFP virus infection at an MOI of 100 at 4 °C. Cells were then further treated with 0.5% DMSO or 1 mM amantadine for 3 hours at 37 °C. Cells were then fixed and stained with the anti-M1 antibody. The number of the cells with dispersed M1 in cytoplasm was quantified and normalized as described in the legend to panel A and B (right panel). (D) vRNP import into the nucleus is impeded by knockdown of ACP2. A549 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs at 37 °C for 48 hours prior to rPR8-GFP infection at an MOI of 100 at 4 °C. Cells were then incubated at 37 °C for 3.5 hours before staining with the anti-NP antibody. The number of the nuclear NP-positive cells was quantified and normalized as described in the legend to panel A and B. Bar graphs show means ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistical significance between the indicated groups was tested using the Student’s t-test with a threshold of: ***p < 0.001.