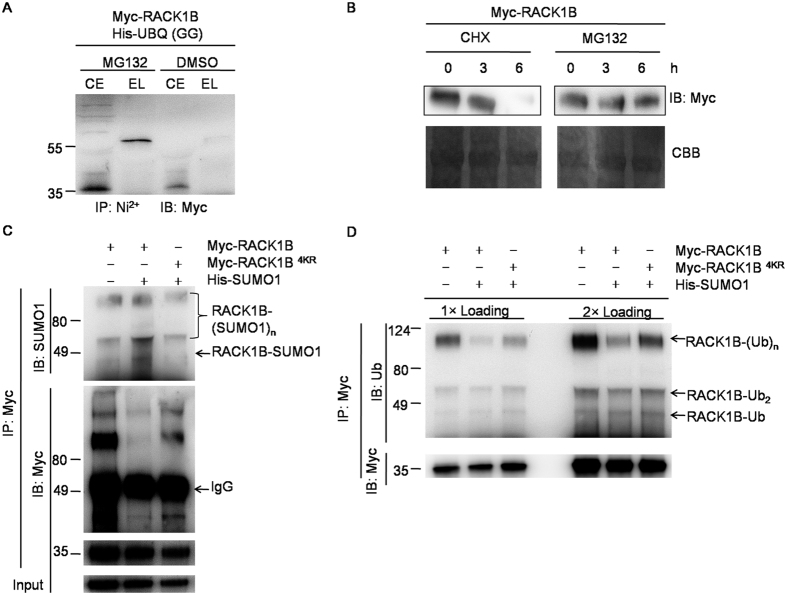
Figure 4. Sumoylation of RACK1B competes with ubiquitination at the same lysine residues.
(A) In vivo ubiquitination assay. 35S::Myc-RACK1B was co-transformed with 35S::His-UBQ(GG) in Col-0 protoplasts and treated with 50 μM MG132 or DMSO for 20 h. The ubiquitination of RACK1B was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibodies. CE, crude extract, EL, elutes from Ni2+-chromatography. (B) Degradation assay. 35S::Myc-RACK1B was transiently expressed in Col-0 protoplasts. After incubation for 20 h, the protoplasts were treated with 100 μM CHX or 50 μM MG132. The degradation rates of RACK1B were compared at the indicated time points. (C,D) In vivo immunoprecipitation assay. 35S::Myc-RACK1B or 35S::Myc-RACK1B4KRwas expressed with or without 35S::His-SUMO1(GG) in Col-0 protoplasts. RACK1B and RACK1B4KR were precipitated using anti-Myc antibodies and subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-SUMO1 (C) or anti-ubiquitin (D) antibodies.